William Pitt, Earl Of Chatham on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham, (15 November 170811 May 1778) was a British statesman of the Whig group who served as
 William's father was
William's father was
 On Pitt's return home it was necessary for him, as the younger son, to choose a profession and he opted for a career in the army. He obtained a
On Pitt's return home it was necessary for him, as the younger son, to choose a profession and he opted for a career in the army. He obtained a
 Walpole and Newcastle were now giving the war in Europe a much higher priority than the colonial conflict with Spain in the Americas.
Walpole and Newcastle were now giving the war in Europe a much higher priority than the colonial conflict with Spain in the Americas.
 Despite his disappointment there was no immediate open breach. Pitt continued at his post; and at the general election which took place during the year he even accepted a nomination for the Duke's
Despite his disappointment there was no immediate open breach. Pitt continued at his post; and at the general election which took place during the year he even accepted a nomination for the Duke's  Eager to prevent the war spreading to Europe, Newcastle now tried to conclude a series of treaties that would secure Britain allies through the payment of subsidies, which he hoped would discourage France from attacking Britain. Similar subsidies had been an issue of past disagreement, and they were widely attacked by Patriot Whigs and Tories. As the government came under increasing attack, Newcastle replaced Robinson with Fox who it was acknowledged carried more political weight and again slighted Pitt.
Finally in November 1755, Pitt was dismissed from office as paymaster, having spoken during a debate at great length against the new system of continental subsidies proposed by the government of which he was still a member. Fox retained his own place, and though the two men continued to be of the same party, and afterwards served again in the same government, there was henceforward a rivalry between them, which makes the celebrated opposition of their sons,
Eager to prevent the war spreading to Europe, Newcastle now tried to conclude a series of treaties that would secure Britain allies through the payment of subsidies, which he hoped would discourage France from attacking Britain. Similar subsidies had been an issue of past disagreement, and they were widely attacked by Patriot Whigs and Tories. As the government came under increasing attack, Newcastle replaced Robinson with Fox who it was acknowledged carried more political weight and again slighted Pitt.
Finally in November 1755, Pitt was dismissed from office as paymaster, having spoken during a debate at great length against the new system of continental subsidies proposed by the government of which he was still a member. Fox retained his own place, and though the two men continued to be of the same party, and afterwards served again in the same government, there was henceforward a rivalry between them, which makes the celebrated opposition of their sons,
 In December 1756, Pitt, who now sat for
In December 1756, Pitt, who now sat for
 A coalition with Newcastle was formed in June 1757, and held power until October 1761. It brought together several various factions and was built around the partnership between Pitt and Newcastle, which a few months earlier had seemed impossible. The two men used
A coalition with Newcastle was formed in June 1757, and held power until October 1761. It brought together several various factions and was built around the partnership between Pitt and Newcastle, which a few months earlier had seemed impossible. The two men used
 In France a new leader, the
In France a new leader, the
 To the preliminaries of the
To the preliminaries of the
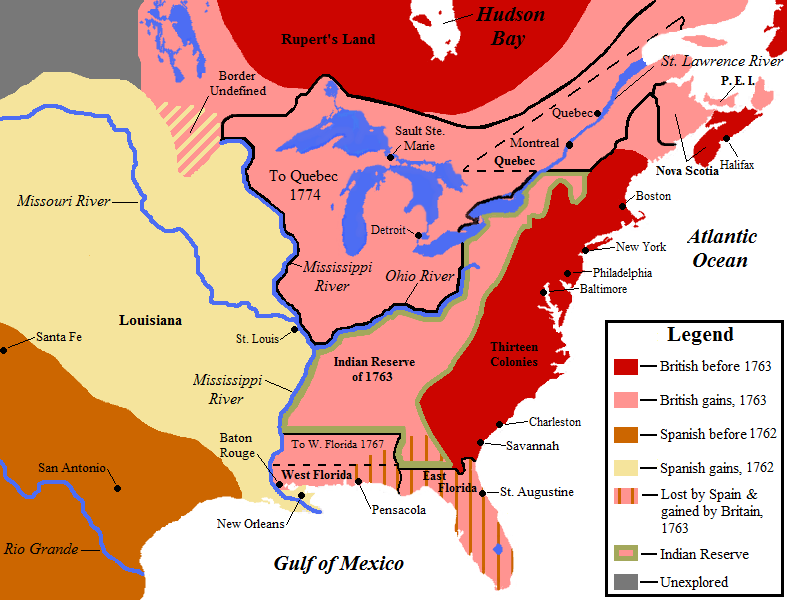
 Pitt's particular genius was to finance an army on the continent to drain French men and resources so that Britain might concentrate on what he held to be the vital spheres: Canada and the
Pitt's particular genius was to finance an army on the continent to drain French men and resources so that Britain might concentrate on what he held to be the vital spheres: Canada and the
 George II died on 25 October 1760, and was succeeded by his grandson,
George II died on 25 October 1760, and was succeeded by his grandson,

 Soon after his resignation a renewed attack of gout freed Chatham from the mental disease under which he had so long suffered. He had been nearly two years and a half in seclusion when, in July 1769, he again appeared in public at a royal levee. It was not, however, until 1770 that he resumed his seat in the House of Lords.
Soon after his resignation a renewed attack of gout freed Chatham from the mental disease under which he had so long suffered. He had been nearly two years and a half in seclusion when, in July 1769, he again appeared in public at a royal levee. It was not, however, until 1770 that he resumed his seat in the House of Lords.
 Pitt had now almost no personal following, mainly owing to the grave mistake he had made in not forming an alliance with the Rockingham party, but his eloquence was as powerful as ever, and all its power was directed against the government policy in the contest with America, which had become the question of all-absorbing interest. His last appearance in the House of Lords was on 7 April 1778, on the occasion of the
Pitt had now almost no personal following, mainly owing to the grave mistake he had made in not forming an alliance with the Rockingham party, but his eloquence was as powerful as ever, and all its power was directed against the government policy in the contest with America, which had become the question of all-absorbing interest. His last appearance in the House of Lords was on 7 April 1778, on the occasion of the

/ref> The American city of
Prime Minister of Great Britain
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern pri ...
from 1766 to 1768. Historians call him Chatham or William Pitt the Elder to distinguish him from his son William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ire ...
, who was also a prime minister. Pitt was also known as the Great Commoner, because of his long-standing refusal to accept a title until 1766.
Pitt was a member of the British cabinet and its informal leader from 1756 to 1761 (with a brief interlude in 1757), during the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
(including the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
in the American colonies). He again led the ministry, holding the official title of Lord Privy Seal
The Lord Privy Seal (or, more formally, the Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal) is the fifth of the Great Officers of State (United Kingdom), Great Officers of State in the United Kingdom, ranking beneath the Lord President of the Council and abov ...
, between 1766 and 1768. Much of his power came from his brilliant oratory. He was out of power for most of his career and became well known for his attacks on the government, such as those on Walpole's corruption in the 1730s, Hanoverian subsidies in the 1740s, peace with France in the 1760s, and the uncompromising policy towards the American colonies in the 1770s.
Pitt is best known as the wartime political leader of Britain in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
, especially for his single-minded devotion to victory over France, a victory which ultimately solidified Britain's dominance over world affairs. He is also known for his popular appeal, his opposition to corruption in government, his support for the American position in the run-up to the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, his advocacy of British greatness, expansionism and empire, and his antagonism towards Britain's chief enemies and rivals for colonial power, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. Marie Peters argues his statesmanship was based on a clear, consistent, and distinct appreciation of the value of the Empire.
The British parliamentary historian P. D. G. Thomas
Peter David Garner Thomas ( 1 May 1930 - 7 July 2020) was a Welsh historian specialising in 18th-century British and American politics.
Thomas was born in Bangor, Wales, and educated at the University College of North Wales and University College ...
argued that Pitt's power was based not on his family connections but on the extraordinary parliamentary skills by which he dominated the House of Commons. He displayed a commanding manner, brilliant rhetoric, and sharp debating skills that cleverly utilised broad literary and historical knowledge. Scholars rank him highly among all British prime ministers.
Early life
Family
Pitt was the grandson ofThomas Pitt
Thomas Pitt (5 July 1653 – 28 April 1726) of Blandford St Mary in Dorset, later of Stratford in Wiltshire and of Boconnoc in Cornwall, known during life commonly as ''Governor Pitt'', as ''Captain Pitt'', or posthumously, as ''"Diamond" ...
(1653–1726), the governor of Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
, known as "Diamond" Pitt for having discovered a diamond of extraordinary size and sold it to the Duke of Orléans
Duke of Orléans (french: Duc d'Orléans) was a French royal title usually granted by the King of France to one of his close relatives (usually a younger brother or son), or otherwise inherited through the male line. First created in 1344 by King ...
for around £135,000. This transaction, as well as other trading deals in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, established the Pitt family fortune. After returning home the Governor was able to raise his family to a position of wealth and political influence: in 1691 he purchased the property of Boconnoc
Boconnoc ( kw, Boskennek) is a civil parishes in England, civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, approximately four miles east of the town of Lostwithiel. According to the UK census 2011, 2011 census the parish had a population of 9 ...
in Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
, which gave him control of a seat in Parliament. He made further land purchases and became one of the dominant political figures in the West Country
The West Country (occasionally Westcountry) is a loosely defined area of South West England, usually taken to include all, some, or parts of the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, Bristol, and, less commonly, Wiltshire, Gloucesters ...
, controlling seats such as the rotten borough
A rotten or pocket borough, also known as a nomination borough or proprietorial borough, was a parliamentary borough or constituency in England, Great Britain, or the United Kingdom before the Reform Act 1832, which had a very small electorat ...
of Old Sarum
Old Sarum, in Wiltshire, South West England, is the now ruined and deserted site of the earliest settlement of Salisbury. Situated on a hill about north of modern Salisbury near the A345 road, the settlement appears in some of the earliest re ...
.
 William's father was
William's father was Robert Pitt
Robert Pitt (1680 – 21 May 1727) was a British politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1705 to 1727. He was the father and grandfather of two prime ministers, William Pitt the elder and William Pitt the younger.
Early life
Pitt was the ...
(1680–1727), the eldest son of Governor Pitt, who served as a Tory
A Tory () is a person who holds a political philosophy known as Toryism, based on a British version of traditionalism and conservatism, which upholds the supremacy of social order as it has evolved in the English culture throughout history. Th ...
Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
from 1705 to 1727. His mother was Harriet Villiers, the daughter of Edward Villiers-FitzGerald and the Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
heiress Katherine FitzGerald. Both William's paternal uncles Thomas
Thomas may refer to:
People
* List of people with given name Thomas
* Thomas (name)
* Thomas (surname)
* Saint Thomas (disambiguation)
* Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church
* Thomas the Ap ...
and John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second ...
were MPs, while his aunt Lucy
Lucy is an English feminine given name derived from the Latin masculine given name Lucius with the meaning ''as of light'' (''born at dawn or daylight'', maybe also ''shiny'', or ''of light complexion''). Alternative spellings are Luci, Luce, Luci ...
married the leading Whig politician and soldier General James Stanhope. From 1717 to 1721, Stanhope served as effective First Minister in the Stanhope–Sunderland Ministry, and was a useful political contact for the Pitt family until the collapse of the South Sea Bubble
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
, a disaster which engulfed the government.
Birth and Education
William Pitt was born atGolden Square
Golden Square, in Soho, the City of Westminster, London, is a mainly hardscaped garden square planted with a few mature trees and raised borders in Central London flanked by classical office buildings. Its four approach ways are north and sout ...
, Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Bu ...
, on 15 November 1708. His older brother Thomas Pitt
Thomas Pitt (5 July 1653 – 28 April 1726) of Blandford St Mary in Dorset, later of Stratford in Wiltshire and of Boconnoc in Cornwall, known during life commonly as ''Governor Pitt'', as ''Captain Pitt'', or posthumously, as ''"Diamond" ...
had been born in 1704. There were also five sisters: Harriet, Catherine, Ann, Elizabeth, and Mary. From 1719 William was educated at Eton College
Eton College () is a public school in Eton, Berkshire, England. It was founded in 1440 by Henry VI under the name ''Kynge's College of Our Ladye of Eton besyde Windesore'',Nevill, p. 3 ff. intended as a sister institution to King's College, C ...
along with his brother. William disliked Eton, later claiming that "a public school
Public school may refer to:
* State school (known as a public school in many countries), a no-fee school, publicly funded and operated by the government
* Public school (United Kingdom), certain elite fee-charging independent schools in England an ...
might suit a boy of turbulent disposition but would not do where there was any gentleness". It was at school that Pitt began to suffer from gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensit ...
. Governor Pitt died in 1726, and the family estate at Boconnoc passed to William's father. When he died the following year, Boconnoc was inherited by William's elder brother, Thomas Pitt of Boconnoc
Thomas Pitt (''c.'' 1705 – 17 July 1761), of Boconnoc, Cornwall, was a British landowner and politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1727 and 1761. He was Lord Warden of the Stannaries from 1742 to 1751.
Pitt was the grandson and ...
.
In January 1727, William was entered as a gentleman commoner
A commoner is a student at certain universities in the British Isles who historically pays for his own tuition and commons, typically contrasted with scholars and exhibitioners, who were given financial emoluments towards their fees.
Cambridge
...
at Trinity College, Oxford
(That which you wish to be secret, tell to nobody)
, named_for = The Holy Trinity
, established =
, sister_college = Churchill College, Cambridge
, president = Dame Hilary Boulding
, location = Broad Street, Oxford OX1 3BH
, coordinates ...
. There is evidence that he was an extensive reader, if not a minutely accurate classical scholar. Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
was his favourite author. William diligently cultivated the faculty of expression by the practice of translation and re-translation. In these years he became a close friend of George Lyttelton, who would later become a leading politician. In 1728 a violent attack of gout compelled him to leave Oxford without finishing his degree. He then chose to travel abroad, from 1728 attending Utrecht University
Utrecht University (UU; nl, Universiteit Utrecht, formerly ''Rijksuniversiteit Utrecht'') is a public research university in Utrecht, Netherlands. Established , it is one of the oldest universities in the Netherlands. In 2018, it had an enrollme ...
in the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, gaining a knowledge of Hugo Grotius
Hugo Grotius (; 10 April 1583 – 28 August 1645), also known as Huig de Groot () and Hugo de Groot (), was a Dutch humanist, diplomat, lawyer, theologian, jurist, poet and playwright.
A teenage intellectual prodigy, he was born in Delft ...
and other writers on international law and diplomacy. It is not known how long Pitt studied at Utrecht; by 1730 he had returned to his brother's estate at Boconnoc.
He had recovered from the attack of gout, but the disease proved intractable, and he continued to be subject to attacks of growing intensity at frequent intervals until his death.
Military career
 On Pitt's return home it was necessary for him, as the younger son, to choose a profession and he opted for a career in the army. He obtained a
On Pitt's return home it was necessary for him, as the younger son, to choose a profession and he opted for a career in the army. He obtained a cornet
The cornet (, ) is a brass instrument similar to the trumpet but distinguished from it by its conical bore, more compact shape, and mellower tone quality. The most common cornet is a transposing instrument in B, though there is also a sopr ...
's commission in the dragoons
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat ...
with the King's Own Regiment of Horse (later 1st King's Dragoon Guards
The 1st King's Dragoon Guards was a cavalry regiment in the British Army. The regiment was raised by Sir John Lanier in 1685 as the 2nd Queen's Regiment of Horse, named in honour of Queen Mary, consort of King James II. It was renamed the 2nd Ki ...
). George II George II or 2 may refer to:
People
* George II of Antioch (seventh century AD)
* George II of Armenia (late ninth century)
* George II of Abkhazia (916–960)
* Patriarch George II of Alexandria (1021–1051)
* George II of Georgia (1072–1089)
* ...
never forgot the jibes of "the terrible cornet of horse". It was reported that the £1,000 cost of the commission had been supplied by Robert Walpole
Robert Walpole, 1st Earl of Orford, (26 August 1676 – 18 March 1745; known between 1725 and 1742 as Sir Robert Walpole) was a British statesman and Whig politician who, as First Lord of the Treasury, Chancellor of the Exchequer, and Leader ...
, the prime minister, out of Treasury
A treasury is either
*A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry.
*A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be state or royal property, church treasure or in p ...
funds in an attempt to secure the support of Pitt's brother Thomas in Parliament. Alternatively the fee may have been waived by the commanding officer of the regiment, Lord Cobham, who was related to the Pitt brothers by marriage.
Pitt was to grow close to Cobham, whom he regarded as almost a surrogate father. He was stationed for much of his service in Northampton
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; ...
, on peacetime duties. Pitt was particularly frustrated that, owing to Walpole's isolationist policies, Britain had not entered the War of the Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession ( pl, Wojna o sukcesję polską; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland, which the other regional power, European powers widened in p ...
which began in 1733, and he had not been able to test himself in battle. Pitt was granted extended leave in 1733, and toured France and Switzerland. He briefly visited Paris but spent most of his time in the French provinces, spending the winter in Lunéville
Lunéville ( ; German, obsolete: ''Lünstadt'' ) is a commune in the northeastern French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle.
It is a subprefecture of the department and lies on the river Meurthe at its confluence with the Vezouze.
History
Lun ...
in the Duchy of Lorraine
The Duchy of Lorraine (french: Lorraine ; german: Lothringen ), originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy.
It was founded in 959 following t ...
.
Pitt's military career was destined to be relatively short. His elder brother Thomas was returned at the general election of 1734 for two separate seats, Okehampton
Okehampton ( ) is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated at the northern edge of Dartmoor, and had a population of 5,922 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards are based i ...
and Old Sarum
Old Sarum, in Wiltshire, South West England, is the now ruined and deserted site of the earliest settlement of Salisbury. Situated on a hill about north of modern Salisbury near the A345 road, the settlement appears in some of the earliest re ...
, and chose to sit for Okehampton, passing the vacant seat to William who accordingly, in February 1735, entered parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
as member for Old Sarum. He became one of a large number of serving army officers in the House of Commons.
Rise to prominence
Patriot Whigs
Pitt soon joined a faction of discontented Whigs known as the Patriots who formed part of the opposition. The group commonly met atStowe House
Stowe House is a grade I listed country house in Stowe, Buckinghamshire, England. It is the home of Stowe School, an independent school and is owned by the Stowe House Preservation Trust who have to date (March 2013) spent more than £25m on th ...
, the country estate of Lord Cobham, who was a leader of the group. Cobham had originally been a supporter of the government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
under Sir Robert Walpole, but a dispute over the controversial Excise Bill
The Excise Bill of 1733 was a proposal by the British government of Robert Walpole to impose an excise tax on a variety of products. This would have allowed Customs officers to search private dwellings to look for contraband untaxed goods. The per ...
of 1733 had seen them join the opposition. Pitt swiftly became one of the faction's most prominent members.
Pitt's maiden speech
A maiden speech is the first speech given by a newly elected or appointed member of a legislature or parliament.
Traditions surrounding maiden speeches vary from country to country. In many Westminster system governments, there is a convention th ...
in the Commons was delivered in April 1736, in the debate on the congratulatory address to George II George II or 2 may refer to:
People
* George II of Antioch (seventh century AD)
* George II of Armenia (late ninth century)
* George II of Abkhazia (916–960)
* Patriarch George II of Alexandria (1021–1051)
* George II of Georgia (1072–1089)
* ...
on the marriage of his son Frederick, Prince of Wales
Frederick, Prince of Wales, (Frederick Louis, ; 31 January 170731 March 1751), was the eldest son and heir apparent of King George II of Great Britain. He grew estranged from his parents, King George and Queen Caroline. Frederick was the fath ...
. He used the occasion to pay compliments, and there was nothing striking in the speech as reported, but it helped to gain him the attention of the House when he later took part on debates on more partisan subjects. In particular, he attacked Britain's non-intervention in the ongoing European war, which he believed was in violation of the Treaty of Vienna and the terms of the Anglo-Austrian Alliance
The Anglo-Austrian Alliance connected the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Habsburg monarchy during the first half of the 18th century. It was largely the work of the British whig statesman Duke of Newcastle, who considered an alliance with Austr ...
.
He became such a troublesome critic of the government that Walpole moved to punish him by arranging his dismissal from the army in 1736, along with several of his friends and political allies. This provoked a wave of hostility to Walpole because many saw such an act as unconstitutional
Constitutionality is said to be the condition of acting in accordance with an applicable constitution; "Webster On Line" the status of a law, a procedure, or an act's accordance with the laws or set forth in the applicable constitution. When l ...
—that members of Parliament were being dismissed for their freedom of speech
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The right to freedom of expression has been recogni ...
in attacking the government, something protected by Parliamentary privilege
Parliamentary privilege is a legal immunity enjoyed by members of certain legislatures, in which legislators are granted protection against civil or criminal liability for actions done or statements made in the course of their legislative duties. ...
. None of the men had their commissions reinstated, however, and the incident brought an end to Pitt's military career. The loss of Pitt's commission was soon compensated. The heir to the throne, Frederick, Prince of Wales
Frederick, Prince of Wales, (Frederick Louis, ; 31 January 170731 March 1751), was the eldest son and heir apparent of King George II of Great Britain. He grew estranged from his parents, King George and Queen Caroline. Frederick was the fath ...
, was involved in a long-running dispute with his father, George II, and was the patron of the opposition
Opposition may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Opposition'' (Altars EP), 2011 EP by Christian metalcore band Altars
* The Opposition (band), a London post-punk band
* ''The Opposition with Jordan Klepper'', a late-night television series on Comed ...
. He appointed Pitt one of his Grooms of the Bedchamber as a reward. In this new position his hostility to the government did not in any degree relax, and his oratorical gifts were substantial.
War
Spanish war
During the 1730s Britain's relationship with Spain had slowly declined. Repeated cases of reported Spanish mistreatment of British merchants, whom they accused of smuggling, caused public outrage, particularly the incident of Jenkins' Ear. Pitt was a leading advocate of a more hard-line policy against Spain, and often castigated Walpole's government for its weakness in dealing withMadrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
. Pitt spoke out against the Convention of El Pardo which aimed to settle the dispute peacefully. In the speech against the Convention in the House of Commons on 8 March 1739 Pitt said:
When trade is at stake, it is your last entrenchment; you must defend it, or perish ... Sir, Spain knows the consequence of a war in America; whoever gains, it must prove fatal to her ... is this any longer a nation? Is this any longer an English Parliament, if with more ships in your harbours than in all the navies of Europe; with above two millions of people in your American colonies, you will bear to hear of the expediency of receiving from Spain an insecure, unsatisfactory, dishonourable Convention?Owing to public pressure, the British government was pushed towards declaring war with Spain in 1739. Britain began with a success at Porto Bello. However the war effort soon stalled, and Pitt alleged that the government was not prosecuting the war effectively—demonstrated by the fact that the British waited two years before taking further offensive action fearing that further British victories would provoke the French into declaring war. When they did so, a failed attack was made on the South American port of Cartagena which left thousands of British troops dead, over half from disease, and cost many ships. The decision to attack during the
rainy season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs.
Rainy Season may also refer to:
* ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King
* "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni
* ''T ...
was held as further evidence of the government's incompetence.
After this, the colonial war against Spain was almost entirely abandoned as British resources were switched towards fighting France in Europe as the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George's W ...
had broken out. The Spanish had repelled a major invasion intended to conquer Central America and succeeded in maintaining their trans-Atlantic convoys while causing much disruption to British shipping and twice broke a British blockade to land troops in Italy, but the war with Spain was treated as a draw. Many of the underlying issues remained unresolved by the later peace treaties leaving the potential for future conflicts to occur. Pitt considered the war a missed opportunity to take advantage of a power in decline, although later he became an advocate of warmer relations with the Spanish in an effort to prevent them forming an alliance with France.
Hanover
 Walpole and Newcastle were now giving the war in Europe a much higher priority than the colonial conflict with Spain in the Americas.
Walpole and Newcastle were now giving the war in Europe a much higher priority than the colonial conflict with Spain in the Americas. Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
went to war in 1740, with many other European states soon joining in. There was a fear that France would launch an invasion of Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
, which was linked to Britain through the crown of George II George II or 2 may refer to:
People
* George II of Antioch (seventh century AD)
* George II of Armenia (late ninth century)
* George II of Abkhazia (916–960)
* Patriarch George II of Alexandria (1021–1051)
* George II of Georgia (1072–1089)
* ...
. To avert this Walpole and Newcastle decided to pay a large subsidy
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
to both Austria and Hanover, in order for them to raise troops and defend themselves.
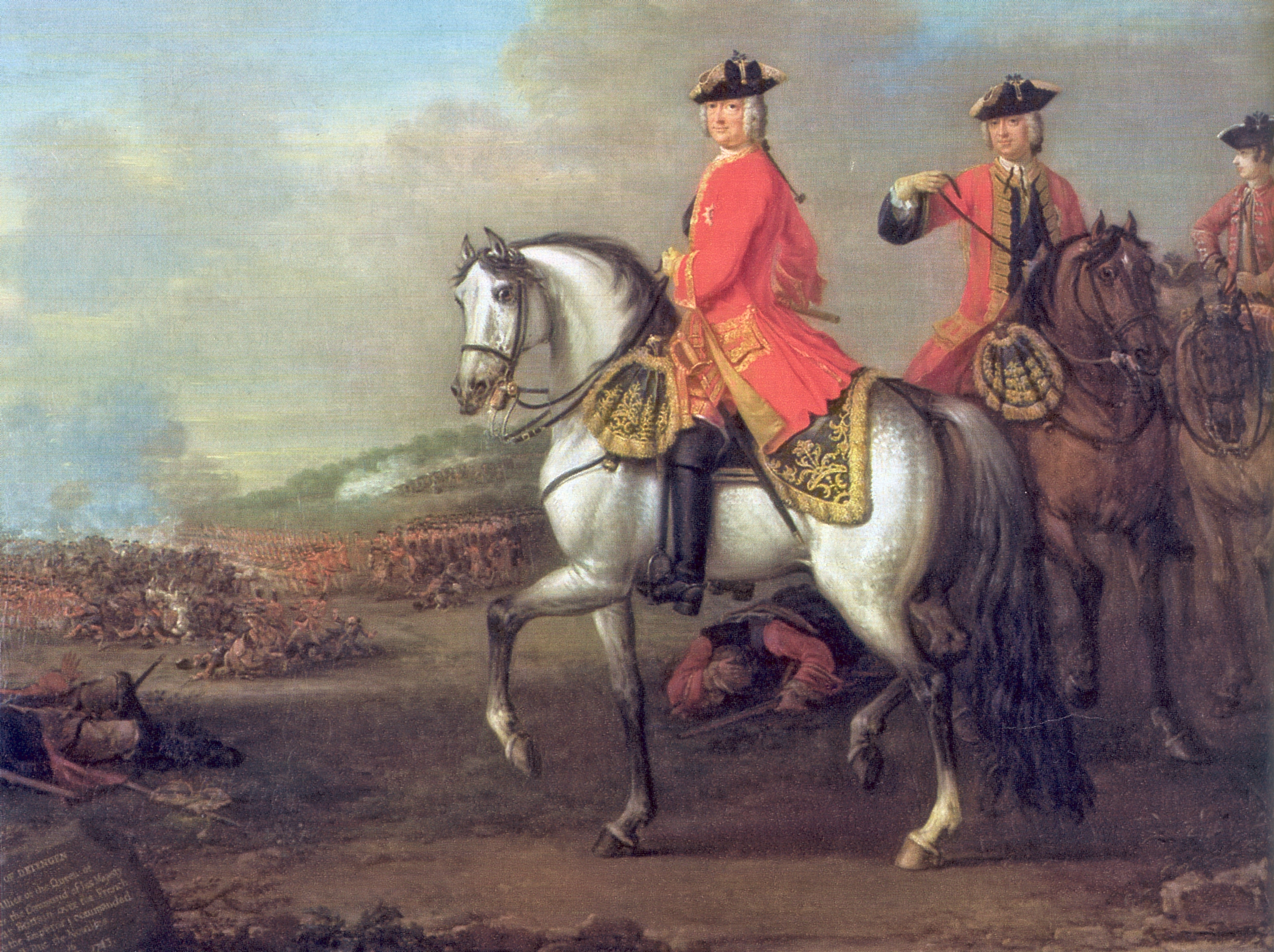
Pitt now launched an attack on such subsidies, playing to widespread anti-Hanoverian feelings in Britain. This boosted his popularity with the public, but earned him the lifelong hatred of the King, who was emotionally committed to Hanover, where he had spent the first thirty years of his life. In response to Pitt's attacks, the British government decided not to pay a direct subsidy to Hanover, but instead to pass the money indirectly through Austriaa move which was considered more politically acceptable. A sizeable Anglo-German army was formed which George II himself led to victory at the Battle of Dettingen
The Battle of Dettingen (german: Schlacht bei Dettingen) took place on 27 June 1743 during the War of the Austrian Succession at Dettingen in the Electorate of Mainz, Holy Roman Empire (now Karlstein am Main in Bavaria). It was fought between a ...
in 1743, reducing the immediate threat to Hanover.
Fall of Walpole
Many of Pitt's attacks on the government were directed personally at Walpole who had now been Prime Minister for twenty years. He spoke in favour of the motion in 1742 for aninquiry
An inquiry (also spelled as enquiry in British English) is any process that has the aim of augmenting knowledge, resolving doubt, or solving a problem. A theory of inquiry is an account of the various types of inquiry and a treatment of the ...
into the last ten years of Walpole's administration. In February 1742, following poor election results and the disaster at Cartagena, Walpole was at last forced to succumb to the long-continued attacks of opposition, resigned and took a peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks.
Peerages include:
Australia
* Australian peers
Belgium
* Belgi ...
.
Pitt now expected a new government to be formed led by Pulteney and dominated by Tories
A Tory () is a person who holds a political philosophy known as Toryism, based on a British version of traditionalism and conservatism, which upholds the supremacy of social order as it has evolved in the English culture throughout history. Th ...
and Patriot Whigs
The Patriot Whigs, later the Patriot Party, were a group within the Whig Party in Great Britain from 1725 to 1803. The group was formed in opposition to the government of Robert Walpole in the House of Commons in 1725, when William Pulteney (l ...
in which he could expect a junior position. Walpole was instead succeeded as Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
by Lord Wilmington
Spencer Compton, 1st Earl of Wilmington, (2 July 1743) was a British Whig statesman who served continuously in government from 1715 until his death. He sat in the English and British House of Commons between 1698 and 1728, and was then raise ...
, though the real power in the new government was divided between Lord Carteret
John Carteret, 2nd Earl Granville, 7th Seigneur of Sark, (; 22 April 16902 January 1763), commonly known by his earlier title Lord Carteret, was a British statesman and Lord President of the Council from 1751 to 1763; he worked extremely close ...
and the Pelham brothers (Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
*Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
and Thomas, Duke of Newcastle). Walpole had carefully orchestrated this new government as a continuance of his own, and continued to advise it up to his death in 1745. Pitt's hopes for a place in the government were thwarted, and he remained in opposition. He was therefore unable to make any personal gain from the downfall of Walpole, to which he had personally contributed a great deal.
The administration formed by the Pelhams in 1744, after the dismissal of Carteret, included many of Pitt's former Patriot allies, but Pitt was not granted a position because of continued ill-feeling by the King and leading Whigs about his views on Hanover. In 1744 Pitt received a large boost to his personal fortune when the Dowager Duchess of Marlborough died leaving him a legacy
In law, a legacy is something held and transferred to someone as their inheritance, as by will and testament. Personal effects, family property, marriage property or collective property gained by will of real property.
Legacy or legacies may refer ...
of £10,000 as an "acknowledgment of the noble defence he had made for the support of the laws of England and to prevent the ruin of his country". It was probably as much a mark of her dislike of Walpole as of her admiration of Pitt.
In Government
Paymaster of the Forces
Reluctantly the King finally agreed to give Pitt a place in the government. Pitt had changed his stance on a number of issues to make himself more acceptable to George, most notably the heated issue of Hanoverian subsidies. To force the matter, the Pelham brothers had to resign on the question whether he should be admitted or not, and it was only after all other arrangements had proved impracticable, that they were reinstated with Pitt appointed asVice Treasurer of Ireland
A vice is a practice, behaviour, or Habit (psychology), habit generally considered immorality, immoral, sinful, crime, criminal, rude, taboo, depraved, degrading, deviant or perverted in the associated society. In more minor usage, vice can refe ...
in February 1746. George continued to resent him however.
In May of the same year Pitt was promoted to the more important and lucrative office of paymaster-general
His Majesty's Paymaster General or HM Paymaster General is a ministerial position in the Cabinet Office of the United Kingdom. The incumbent Paymaster General is Jeremy Quin MP.
History
The post was created in 1836 by the merger of the posit ...
, which gave him a place in the Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mon ...
, though not in the cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
. Here he had an opportunity of displaying his public spirit and integrity in a way that deeply impressed both the king and the country. It had been the usual practise of previous paymasters to appropriate to themselves the interest of all money lying in their hands by way of advance, and also to accept a commission of % on all foreign subsidies. Although there was no strong public sentiment against the practice, Pitt completely refused to profit by it. All advances were lodged by him in the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
until required, and all subsidies were paid over without deduction, even though it was pressed upon him, so that he did not draw a shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence o ...
from his office beyond the salary
A salary is a form of periodic payment from an employer to an employee, which may be specified in an employment contract. It is contrasted with piece wages, where each job, hour or other unit is paid separately, rather than on a periodic basis.
...
legally attaching to it. Pitt ostentatiously made this clear to everyone, although he was in fact following what Henry Pelham
Henry Pelham (25 September 1694 – 6 March 1754) was a British Whig statesman who served as 3rd Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1743 until his death in 1754. He was the younger brother of Thomas Pelham-Holles, 1st Duke of Newcastle, who ...
had done when he had held the post between 1730 and 1743. This helped to establish Pitt's reputation with the British people for honesty and placing the interests of the nation before his own.
The administration formed in 1746 lasted without major changes until 1754. It would appear from his published correspondence that Pitt had a greater influence in shaping its policy than his comparatively subordinate position would in itself have entitled him to. His support for measures, such as the Spanish Treaty and the continental subsidies, which he had violently denounced when in opposition was criticised by his enemies as an example of his political opportunism
Opportunism is the practice of taking advantage of circumstances – with little regard for principles or with what the consequences are for others. Opportunist actions are expedient actions guided primarily by self-interested motives. The term ...
.
Between 1746 and 1748 Pitt worked closely with Newcastle in formulating British military and diplomatic strategy. He shared with Newcastle a belief that Britain should continue to fight until it could receive generous peace terms, in contrast to some such as Henry Pelham
Henry Pelham (25 September 1694 – 6 March 1754) was a British Whig statesman who served as 3rd Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1743 until his death in 1754. He was the younger brother of Thomas Pelham-Holles, 1st Duke of Newcastle, who ...
who favoured an immediate peace. Pitt was personally saddened when his friend and brother-in-law Thomas Grenville
Thomas Grenville (31 December 1755 – 17 December 1846) was a British politician and bibliophile.
Background and education
Grenville was the second son of Prime Minister George Grenville and Elizabeth Wyndham, daughter of Sir William Wyndh ...
was killed at the naval First Battle of Cape Finisterre
The First Battle of Cape Finisterre (14 May 1747in the Julian calendar then in use in Britain this was 3 May 1747) was waged during the War of the Austrian Succession. It refers to the attack by 14 British ships of the line under Admiral Georg ...
in 1747. However, this victory helped secure British supremacy of the sea which gave the British a stronger negotiating position when it came to the peace talks that ended the war. At the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748 British colonial conquests were exchanged for a French withdrawal from Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
. Many saw this as merely an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the La ...
and awaited an imminent new war.
Dispute with Newcastle
In 1754, Henry Pelham died suddenly, and was succeeded as Prime Minister by his brother, the Duke of Newcastle. As Newcastle sat in theHouse of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
, he required a leading politician to represent the government in the House of Commons. Pitt and Henry Fox were considered the two favourites for the position, but Newcastle instead rejected them both and turned to the less well-known figure of Sir Thomas Robinson Thomas, Tom or Tommy Robinson may refer to:
Artists
* Thomas Robinson (composer) (c. 1560 – after 1609), English composer and music teacher
* Thomas Heath Robinson (1869–1954), British book illustrator
Politicians
* Thomas Robinson, 1st Baron ...
, a career diplomat
A diplomat (from grc, δίπλωμα; romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state or an intergovernmental institution such as the United Nations or the European Union to conduct diplomacy with one or more other states or internati ...
, to fill the post. It was widely believed that Newcastle had done this because he feared the ambitions of both Pitt and Fox, and believed he would find it easier to dominate the inexperienced Robinson.
 Despite his disappointment there was no immediate open breach. Pitt continued at his post; and at the general election which took place during the year he even accepted a nomination for the Duke's
Despite his disappointment there was no immediate open breach. Pitt continued at his post; and at the general election which took place during the year he even accepted a nomination for the Duke's pocket borough
A rotten or pocket borough, also known as a nomination borough or proprietorial borough, was a parliamentary borough or constituency in England, Great Britain, or the United Kingdom before the Reform Act 1832, which had a very small electorat ...
of Aldborough. He had sat for Seaford since 1747. The government won a landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
, further strengthening its majority in parliament.
When parliament met, however, he made no secret of his feelings. Ignoring Robinson, Pitt made frequent and vehement attacks on Newcastle himself, though still continued to serve as Paymaster under him. From 1754 Britain was increasingly drawn into conflict with France during this period, despite Newcastle's wish to maintain the peace. The countries clashed in North America, where each had laid claim to the Ohio Country. A British expedition under General Braddock had been despatched and defeated in summer 1755 which caused a ratcheting up of tensions.
 Eager to prevent the war spreading to Europe, Newcastle now tried to conclude a series of treaties that would secure Britain allies through the payment of subsidies, which he hoped would discourage France from attacking Britain. Similar subsidies had been an issue of past disagreement, and they were widely attacked by Patriot Whigs and Tories. As the government came under increasing attack, Newcastle replaced Robinson with Fox who it was acknowledged carried more political weight and again slighted Pitt.
Finally in November 1755, Pitt was dismissed from office as paymaster, having spoken during a debate at great length against the new system of continental subsidies proposed by the government of which he was still a member. Fox retained his own place, and though the two men continued to be of the same party, and afterwards served again in the same government, there was henceforward a rivalry between them, which makes the celebrated opposition of their sons,
Eager to prevent the war spreading to Europe, Newcastle now tried to conclude a series of treaties that would secure Britain allies through the payment of subsidies, which he hoped would discourage France from attacking Britain. Similar subsidies had been an issue of past disagreement, and they were widely attacked by Patriot Whigs and Tories. As the government came under increasing attack, Newcastle replaced Robinson with Fox who it was acknowledged carried more political weight and again slighted Pitt.
Finally in November 1755, Pitt was dismissed from office as paymaster, having spoken during a debate at great length against the new system of continental subsidies proposed by the government of which he was still a member. Fox retained his own place, and though the two men continued to be of the same party, and afterwards served again in the same government, there was henceforward a rivalry between them, which makes the celebrated opposition of their sons, William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ire ...
and Charles James Fox
Charles James Fox (24 January 1749 – 13 September 1806), styled ''The Honourable'' from 1762, was a prominent British Whig statesman whose parliamentary career spanned 38 years of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. He was the arch-riv ...
, seem like an inherited quarrel.
Pitt's relationship with the Duke slumped further in early 1756 when he alleged that Newcastle was deliberately leaving the island of Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capi ...
ill-defended so that the French would seize it, and Newcastle could use its loss to prove that Britain was not able to fight a war against France and sue for peace. When in June 1756 Menorca fell after a failed attempt by Admiral Byng to relieve it, Pitt's allegations fuelled the public anger against Newcastle, leading him to be attacked by a mob in Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich ...
. The loss of Menorca shattered public faith in Newcastle, and forced him to step down as Prime Minister in November 1756.
Secretary of State
 In December 1756, Pitt, who now sat for
In December 1756, Pitt, who now sat for Okehampton
Okehampton ( ) is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated at the northern edge of Dartmoor, and had a population of 5,922 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards are based i ...
, became Secretary of State for the Southern Department
The Secretary of State for the Southern Department was a position in the cabinet of the government of the Kingdom of Great Britain up to 1782, when the Southern Department became the Home Office.
History
Before 1782, the responsibilities of ...
, and Leader of the House of Commons
The leader of the House of Commons is a minister of the Crown of the Government of the United Kingdom whose main role is organising government business in the House of Commons. The leader is generally a member or attendee of the cabinet of the ...
under the premiership of the Duke of Devonshire
Duke of Devonshire is a title in the Peerage of England held by members of the Cavendish family. This (now the senior) branch of the Cavendish family has been one of the wealthiest British aristocratic families since the 16th century and has be ...
. Upon entering this coalition, Pitt said to Devonshire: "My Lord, I am sure I can save this country, and no one else can".
He had made it a condition of his joining any administration that Newcastle should be excluded from it, which proved fatal to the lengthened existence of his government. With the king unfriendly, and Newcastle, whose influence was still dominant in the Commons, estranged, it was impossible to carry on a government by the aid of public opinion alone, however emphatically that might have declared itself on his side. The historian Basil Williams has claimed that this is the first time in British history when a "man was called to supreme power by the voice of the people" rather than by the king's appointment or as the choice of Parliament.
Pitt drew up his plans for the campaigning season of 1757 in which he hoped to reverse Britain's string of defeats during the war's opening years.
In April 1757 Pitt was dismissed from office on account of his opposition to the continental policy and the circumstances surrounding the court-martial and execution of Admiral John Byng
Admiral John Byng (baptised 29 October 1704 – 14 March 1757) was a British Royal Navy officer who was court-martialled and executed by firing squad. After joining the navy at the age of thirteen, he participated at the Battle of Cape Passa ...
. He was succeeded by the Duke of Devonshire who formed the 1757 Caretaker Ministry
The Kingdom of Great Britain was governed by a caretaker government in April–June 1757—after the King's dismissal of William Pitt led to the collapse of the Pitt–Devonshire ministry amid the Seven Years' War. William Cavendis ...
. But the power that was insufficient to keep him in office was strong enough to make any arrangement that excluded him impracticable. The public voice spoke in a way that was not to be mistaken. Probably no English minister ever received in so short a time so many proofs of the confidence and admiration of the public, the capital and all the chief towns voting him addresses and the freedom of their corporations (e.g., London presented him with the first ever ''honorary'' Freedom
Freedom is understood as either having the ability to act or change without constraint or to possess the power and resources to fulfill one's purposes unhindered. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving on ...
of the City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
awarded in history). Horace Walpole
Horatio Walpole (), 4th Earl of Orford (24 September 1717 – 2 March 1797), better known as Horace Walpole, was an English writer, art historian, man of letters, antiquarian, and Whigs (British political party), Whig politician.
He had Strawb ...
recorded the freedoms of various cities awarded to Pitt:
... for some weeks it rained gold boxes:After some weeks' negotiation, in the course of which the firmness and moderation of "''The Great Commoner''", as he had come to be called, contrasted favourably with the characteristic tortuosities of the crafty peer, matters were settled on such a basis that, while Newcastle was the nominal, Pitt was the virtual head of the government. On his acceptance of office, he was chosen member forChester Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...,Worcester Worcester may refer to: Places United Kingdom * Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England ** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament * Worcester Park, London, Englan ...,Norwich Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the See of Norwich, with ...,Bedford Bedford is a market town in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 Census, the population of the Bedford built-up area (including Biddenham and Kempston) was 106,940, making it the second-largest settlement in Bedfordshire, behind Luton, whilst ...,Salisbury Salisbury ( ) is a cathedral city in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers Avon, Nadder and Bourne. The city is approximately from Southampton and from Bath. Salisbury is in the southeast of Wil ...,Yarmouth Yarmouth may refer to: Places Canada *Yarmouth County, Nova Scotia **Yarmouth, Nova Scotia **Municipality of the District of Yarmouth **Yarmouth (provincial electoral district) **Yarmouth (electoral district) * Yarmouth Township, Ontario *New ...,Tewkesbury Tewkesbury ( ) is a medieval market town and civil parish in the north of Gloucestershire, England. The town has significant history in the Wars of the Roses and grew since the building of Tewkesbury Abbey. It stands at the confluence of the Riv ...,Newcastle-on-Tyne Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is als ...,Stirling Stirling (; sco, Stirlin; gd, Sruighlea ) is a city in central Scotland, northeast of Glasgow and north-west of Edinburgh. The market town, surrounded by rich farmland, grew up connecting the royal citadel, the medieval old town with its me ..., and other populous and chief towns following the example.Exeter Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol. In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ..., with singular affection, sent boxes of oak.
Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
.
Pitt–Newcastle ministry
 A coalition with Newcastle was formed in June 1757, and held power until October 1761. It brought together several various factions and was built around the partnership between Pitt and Newcastle, which a few months earlier had seemed impossible. The two men used
A coalition with Newcastle was formed in June 1757, and held power until October 1761. It brought together several various factions and was built around the partnership between Pitt and Newcastle, which a few months earlier had seemed impossible. The two men used Lord Chesterfield
Philip Dormer Stanhope, 4th Earl of Chesterfield, (22 September 169424 March 1773) was a British statesman, diplomat, and man of letters, and an acclaimed wit of his time.
Early life
He was born in London to Philip Stanhope, 3rd Earl of Ches ...
as an intermediary and had managed to agree a division of powers that was acceptable to both. For the past few months Britain had been virtually leaderless, although Devonshire had remained formally Prime Minister, but now Pitt and Newcastle were ready to offer stronger direction to the country's strategy.
By summer 1757 the British war effort over the previous three years had broadly been a failure. Britain's attempts to take the offensive in North America had ended in disaster, Menorca had been lost, and the Duke of Cumberland
Duke of Cumberland is a peerage title that was conferred upon junior members of the British Royal Family, named after the historic county of Cumberland.
History
The Earldom of Cumberland, created in 1525, became extinct in 1643. The dukedo ...
's Army of Observation An army of observation is a military body whose purpose is to monitor a given area or enemy body in preparation for possible hostilities.
Some of the more notable armies of observation include:
*Third Reserve Army of Observation, a Russian army tas ...
was retreating across Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
following the Battle of Hastenback
The Battle of Hastenbeck (26 July 1757) was fought as part of the Invasion of Hanover during the Seven Years' War between the allied forces of Hanover, Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel) and Brunswick, and the French. The allies were defeated by ...
. In October Cumberland was forced to conclude the Convention of Klosterzeven
The Convention of Klosterzeven (or the Convention of Kloster-Zeven, german: Konvention von Kloster Zeven) was a convention signed on 10 September 1757 at Klosterzeven between France and the Electorate of Hanover during the Seven Years' War that ...
, which would take Hanover out of the war. The French Invasion of Hanover posed a threat to Britain's ally Prussia, which was now vulnerable to attack from the west by the French as well as facing attack from Austria, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
and Sweden.
Although it was late in the campaigning season when he had come to power, Pitt set about trying to initiate a more assertive strategy. He conspired with a number of figures to persuade the Hanoverians to revoke the Klosterzevern Convention and re-enter the war on Britain's side, which they did in late 1757. He also put into practice a scheme of Naval Descents
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducted ...
that would make amphibious
Amphibious means able to use either land or water. In particular it may refer to:
Animals
* Amphibian, a vertebrate animal of the class Amphibia (many of which live on land and breed in water)
* Amphibious caterpillar
* Amphibious fish, a fish ...
landings on the French coast. The first of these, the Raid on Rochefort
The Raid on Rochefort (or Descent on Rochefort) was a British amphibious attempt to capture the French Atlantic port of Rochefort in September 1757 during the Seven Years' War. The raid pioneered a new tactic of "descents" on the French coast ...
, took place in September but was not a success. The centrepiece of the campaign in North America, an expedition to capture Louisbourg, was aborted due to the presence of a large French fleet and a gale that scattered the British fleet.
1758
In 1758 Pitt began to put into practice a new strategy to win the Seven Years' War, which would involve tying down large numbers of French troops and resources in Germany, while Britain used its naval supremacy to launch expeditions to capture French forces around the globe. Following the capture of Emden he ordered the dispatch of the first British troops to the European continent under theDuke of Marlborough
General (United Kingdom), General John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, 1st Prince of Mindelheim, 1st Count of Nellenburg, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, (26 May 1650 – 16 June 1722 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) was an Engl ...
, who joined Brunswick's army. This was a dramatic reversal of his previous position, as he had recently been strongly opposed to any such commitment.
Pitt had been lobbied by an American merchant Thomas Cumming
Thomas Cumming was an Thirteen Colonies, American merchant of the 18th century who built up a large commercial empire in West Africa. He is best known for the role he played in the 1758 Capture of Senegal in which he submitted a plan to the Brit ...
to launch an expedition against the French trading settlements in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
. In April 1758 British forces captured the ill-defended fort of Saint-Louis in Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
. The mission was so lucrative that Pitt sent out further expeditions to capture Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; Wolof: Beer Dun) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade ...
and Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
later in the year. He also drew up plans to attack French islands in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
the following year at the suggestion of a Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
n sugar planter William Beckford.
In North America, a second British attempt to capture Louisbourg
Louisbourg is an unincorporated community and former town in Cape Breton Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia.
History
The French military founded the Fortress of Louisbourg in 1713 and its fortified seaport on the southwest part of the harbour, ...
succeeded. However, Pitt's pleasure over this was tempered by the subsequent news of a significant British defeat at the Battle of Carillon
The Battle of Carillon, also known as the 1758 Battle of Ticonderoga, Chartrand (2000), p. 57 was fought on July 8, 1758, during the French and Indian War (which was part of the global Seven Years' War). It was fought near Fort Carillon (now k ...
. Towards the end of the year the Forbes Expedition
The Forbes Expedition was a British military expedition to capture Fort Duquesne, led by Brigadier-General John Forbes in 1758, during the French and Indian War. While advancing to the fort, the expedition built the now historic trail, the Forbes ...
seized the site of Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
and began constructing a British settlement that would become known as Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
. This gave the British control of the Ohio Country, which had been the principal cause of the war.
In Europe, Brunswick's forces enjoyed a mixed year. Brunswick had crossed the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, but faced with being cut off he had retreated and blocked any potential French move towards Hanover with his victory at the Battle of Krefeld
The Battle of Krefeld (sometimes referred to by its French name of Créfeld) was a battle fought at Krefeld near the Rhine on 23 June 1758 between a Prussian- Hanoverian army and a French army during the Seven Years' War.
Background
The Hano ...
. The year ended with something approaching a stalemate in Germany. Pitt had continued his naval descents during 1758, but the first had enjoyed only limited success and the second ended with near disaster at the Battle of St Cast
The Battle of Saint Cast was a military engagement during the Seven Years' War on the French coast between British naval and land expeditionary forces and French coastal defence forces. Fought on 11 September 1758, it was won by the French.
Du ...
and no further descents were planned. Instead the troops and ships would be used as part of the coming expedition to the French West Indies
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloupe, ...
. The scheme of amphibious raids was the only one of Pitt's policies during the war that was broadly a failure, although it did help briefly relieve pressure on the German front by tying down French troops on coastal protection service.
Annus Mirabilis
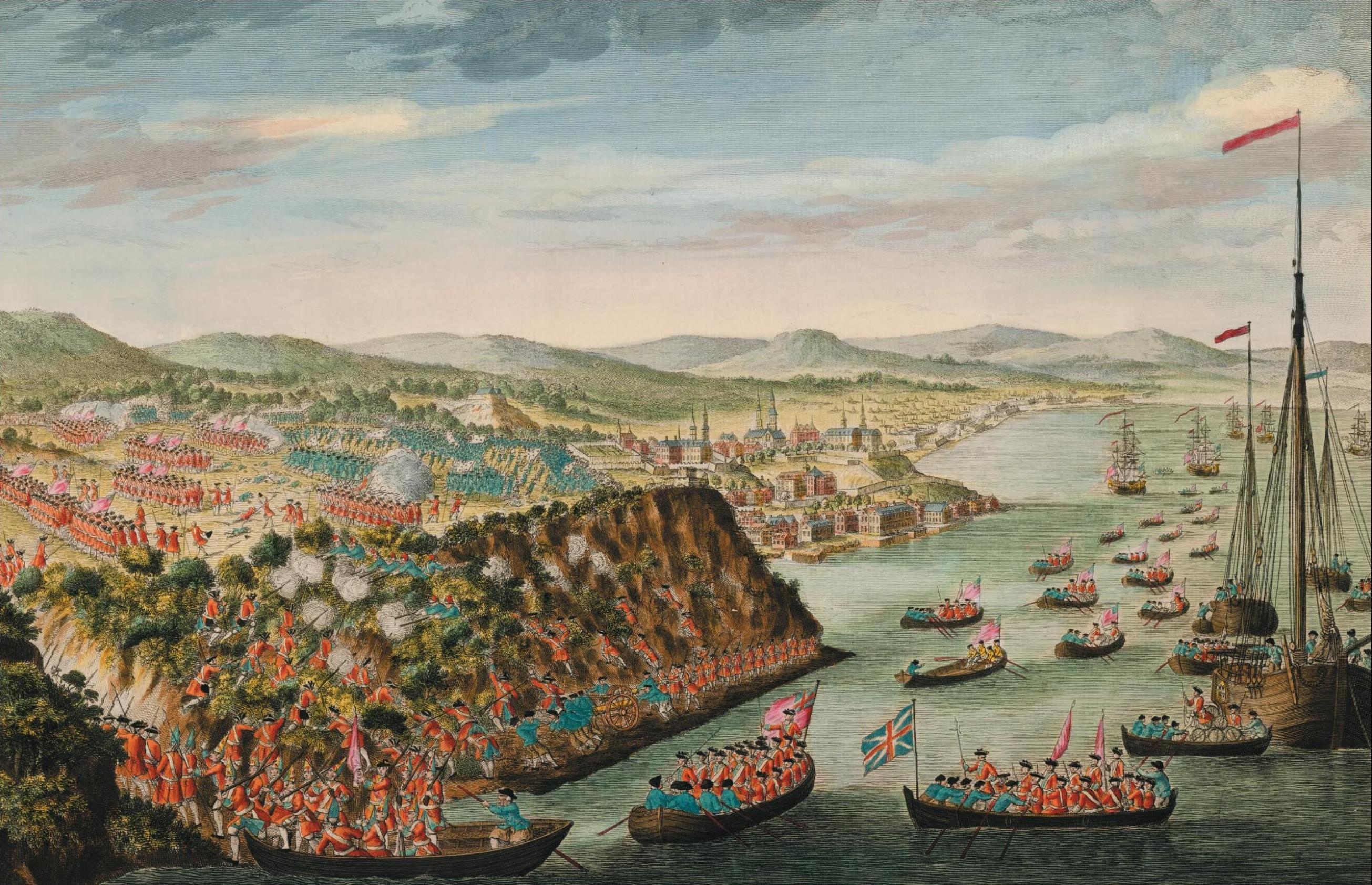
 In France a new leader, the
In France a new leader, the Duc de Choiseul {{Unreferenced, date=April 2019
Choiseul is an illustrious noble family from Champagne, France, descendants of the comtes of Langres. The family's head was Renaud III de Choiseul, comte de Langres and sire de Choiseul, who in 1182 married Alix ...
, had recently come to power and 1759 offered a duel between their rival strategies. Pitt intended to continue with his plan of tying down French forces in Germany while continuing the assault on France's colonies. Choiseul hoped to repel the attacks in the colonies while seeking total victory in Europe.
Pitt's war around the world was largely successful. While a British invasion of Martinique failed, they captured Guadeloupe shortly afterwards. In India, a French attempt to capture Madras was repulsed. In North America, British troops closed in on France's Canadian heartland. A British force under James Wolfe
James Wolfe (2 January 1727 – 13 September 1759) was a British Army officer known for his training reforms and, as a Major-general (United Kingdom), major general, remembered chiefly for his victory in 1759 over the Kingdom of France, French ...
moved up the Saint Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence ( la, Laurentius, lit. "Laurel wreath, laurelled"; 31 December AD 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, perse ...
with the aim of capturing Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
. After initially failing to penetrate the French defences at the Montmorency Falls
The Montmorency Falls (french: Chute Montmorency) is a large waterfall on the Montmorency River in Quebec, Canada.
Location
The falls are located on the boundary between the borough of Beauport, and Boischatel, about from the heart of old Que ...
, Wolfe later led his men to a victory to the west of the city allowing the British forces to capture Quebec.
Choiseul had pinned much of his hopes on a French invasion of Britain, which he hoped would knock Britain out of the war and make it surrender the colonies it had taken from France. Pitt had stripped the home islands of troops to send on his expeditions, leaving Britain guarded by poorly trained militia and giving an opportunity for the French if they could land in enough force. The French did build a large invasion force. However the French naval defeats at Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
and Quiberon Bay
Quiberon Bay (french: Baie de Quiberon) is an area of sheltered water on the south coast of Brittany. The bay is in the Morbihan département.
Geography
The bay is roughly triangular in shape, open to the south with the Gulf of Morbihan to t ...
forced Choiseul to abandon the invasion plans. France's other great hope, that their armies could make a breakthrough in Germany and invade Hanover, was thwarted at the Battle of Minden
The Battle of Minden was a major engagement during the Seven Years' War, fought on 1 August 1759. An Anglo-German army under the overall command of Prussian Field Marshal Ferdinand of Brunswick defeated a French army commanded by Marshal of F ...
. Britain ended the year victorious in every theatre of operations in which it was engaged, with Pitt receiving the credit for this.
1760–61
Britain completed theconquest of Canada
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent ...
in 1760 by capturing Montreal, which effectively brought the war to an end on mainland North America.
Pitt's power had now reached its peak, but was soon under threat. The domestic political situation was altered dramatically when George II died in October 1760. He was succeeded by his grandson, George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
, who had once considered Pitt an ally but had become angered by Pitt's alliance with Newcastle and acceptance of the need for British intervention in Germanywhich George was strongly opposed to. The new king successfully lobbied for his favourite Lord Bute
John Stuart, 3rd Earl of Bute, (; 25 May 1713 – 10 March 1792), styled Lord Mount Stuart between 1713 and 1723, was a British nobleman who served as the 7th Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1762 to 1763 under George III. He was arguabl ...
to be given the post of Northern Secretary
The Secretary of State for the Northern Department was a position in the Cabinet of the government of Great Britain up to 1782, when the Northern Department became the Foreign Office.
History
Before the Act of Union, 1707, the Secretary of S ...
. Bute was inclined to support a withdrawal from Germany, and to fight the war with France largely at sea and in the colonies.
Pitt's plan for an expedition to capture Belle Île
Belle-Île, Belle-Île-en-Mer, or Belle Isle ( br, Ar Gerveur, ; br, label=Old Breton, Guedel) is a French island off the coast of Brittany in the ''département'' of Morbihan, and the largest of Brittany's islands. It is from the Quiberon pe ...
was put into force in April 1761 and it was captured after a siege. This provided yet a further blow to French prestige, as it was the first part of Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
to be occupied. Pitt now expected France to offer terms, although he was prepared for a longer war if necessary. Envoys were exchanged, but neither side could reach an agreement. Pitt's refusal to grant the French a share in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
proved the biggest obstacle to peace, as Pitt declared he would rather lose the use of his right arm than give the French a share there and later said he would rather give up the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is separa ...
than Newfoundland. Newfoundland was at the time seen as possessing huge economic and strategic value because of the extensive fishing industry there.
The war in Germany continued through 1761 with the French again attempting to overcome Brunswick and invade Hanover, but suffering a defeat at the Battle of Villinghausen
The Battle of Villinghausen (or Vellinghausen, also known as the Battle of Kirchdenkern) was a battle in the Seven Years' War fought on the 15th and 16 July 1761 in the western area of present-day Germany, between a large French army and an An ...
. Pitt had substantially increased the number of British troops serving with Brunswick, and he also planned further conquests in the West Indies. A strategy he hoped would compel the French to conclude a reasonable peace treaty.
Treaty of Paris
 To the preliminaries of the
To the preliminaries of the peace
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
concluded in February 1763 he offered an indignant resistance, considering the terms quite inadequate to the successes that had been gained by the country. When the treaty was discussed in parliament in December of the previous year, though suffering from a severe attack of gout, he was carried down to the House, and in a speech of three hours' duration, interrupted more than once by paroxysms of pain, he strongly protested against its various conditions. These conditions included the return of the sugar islands (but Britain retained Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
); trading stations in West Africa (won by Boscawen); Pondicherry
Pondicherry (), now known as Puducherry ( French: Pondichéry ʊdʊˈtʃɛɹi(listen), on-dicherry, is the capital and the most populous city of the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the sout ...
( France's Indian colony); and fishing rights in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
. Pitt's opposition arose through two heads: France had been given the means to become once more formidable at sea, whilst Frederick of Prussia had been betrayed.
Pitt believed that the task had been left half-finished and called for a final year of war which would crush French power for good. Pitt had long-held plans for further conquests which had been uncompleted. Newcastle, by contrast, sought peace but only if the war in Germany could be brought to an honourable and satisfactory conclusion (rather than Britain suddenly bailing out of it as Bute proposed). However the combined opposition of Newcastle and Pitt was not enough to prevent the Treaty passing comfortably in both Houses of Parliament.
However, there were strong reasons for concluding the peace: the National Debt had increased from £74.5m. in 1755 to £133.25m. in 1763, the year of the peace
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
. The requirement to pay down this debt, and the lack of French threat in Canada, were major movers in the subsequent American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
.
The physical cause which rendered this effort so painful probably accounts for the infrequency of his appearances in parliament, as well as for much that is otherwise inexplicable in his subsequent conduct. In 1763 he spoke against the unpopular tax on cider, imposed by his brother-in-law, George Grenville
George Grenville (14 October 1712 – 13 November 1770) was a British Whig statesman who rose to the position of Prime Minister of Great Britain. Grenville was born into an influential political family and first entered Parliament in 1741 as an ...
, and his opposition, though unsuccessful in the House, helped to keep alive his popularity with the country, which cordially hated the excise
file:Lincoln Beer Stamp 1871.JPG, upright=1.2, 1871 U.S. Revenue stamp for 1/6 barrel of beer. Brewers would receive the stamp sheets, cut them into individual stamps, cancel them, and paste them over the Bunghole, bung of the beer barrel so when ...
and all connected with it. When next year the question of general warrant
A writ of assistance is a written order (a writ) issued by a court instructing a law enforcement official, such as a sheriff or a tax collector, to perform a certain task. Historically, several types of writs have been called "writs of assistance ...
s was raised in connexion with the case of John Wilkes
John Wilkes (17 October 1725 – 26 December 1797) was an English radical journalist and politician, as well as a magistrate, essayist and soldier. He was first elected a Member of Parliament in 1757. In the Middlesex election dispute, he fo ...
, Pitt vigorously maintained their illegality, thus defending at once the privileges of Parliament and the freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic News media, media, especially publication, published materials, should be conside ...
.
During 1765 he seems to have been totally incapacitated for public business. In the following year he supported with great power the proposal of the Rockingham administration for the repeal of the Stamp Act, arguing that it was unconstitutional to impose taxes upon the colonies. He thus endorsed the contention of the colonists on the ground of principle, while the majority of those who acted with him contented themselves with resisting the disastrous taxation scheme on the ground of expediency.
The Repeal (1766) of the Stamp Act, indeed, was only passed ''pari passu
''Pari passu'' is a Latin phrase that literally means "with an equal step" or "on equal footing". It is sometimes translated as "ranking equally", "hand-in-hand", "with equal force", or "moving together", and by extension, "fairly", "without pa ...
'' with another censuring the American assemblies, and declaring the authority of the British parliament over the colonies "in all cases whatsoever". Thus the House of Commons repudiated in the most formal manner the principle Pitt laid down. His language in approval of the resistance of the colonists was unusually bold, and perhaps no one but himself could have employed it with impunity at a time when the freedom of debate was only imperfectly conceded.
Pitt had not been long out of office when he was solicited to return to it, and the solicitations were more than once renewed. Unsuccessful overtures were made to him in 1763, and twice in 1765, in May and June—the negotiator in May being the king's uncle, the Duke of Cumberland
Duke of Cumberland is a peerage title that was conferred upon junior members of the British Royal Family, named after the historic county of Cumberland.
History
The Earldom of Cumberland, created in 1525, became extinct in 1643. The dukedo ...
, who went down in person to Hayes, Pitt's seat in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. It is known that he had the opportunity of joining the Marquess of Rockingham's short-lived administration at any time on his own terms, and his conduct in declining an arrangement with that minister has been more generally condemned than any other step in his public life.
Leadership
The ''London Magazine'' of 1767 offered "Pitt, Pompadour, Prussia, Providence" as the reasons for Britain's success in theSeven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
. Pitt's relation to all three was such as to entitle him to a large share in the credit of their deeds. He inspired trust in his chosen commanders by his indifference to rules of seniority—several of "Pitt's boys", like Keppel, captor of Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; Wolof: Beer Dun) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade ...
, were in their thirties—and by his clear orders. It was his discernment that selected Wolfe to lead the attack on Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, and gave him the opportunity of dying a victor on the heights of Abraham
The Heights of Abraham is a tourist attraction in Matlock Bath, Derbyshire, England. It consists of a hilltop park on top of Masson Hill, accessed from the village by either the Heights of Abraham cable car or a steep zig-zag path. The heights ...
. He had personally less to do with the successes in India than with the other great enterprises that shed an undying lustre on his administration; but his generous praise in parliament encouraged Robert Clive
Robert Clive, 1st Baron Clive, (29 September 1725 – 22 November 1774), also known as Clive of India, was the first British Governor of the Bengal Presidency. Clive has been widely credited for laying the foundation of the British ...
, and the forces that acted at the close of the struggle were animated by his indomitable spirit.
 Pitt's particular genius was to finance an army on the continent to drain French men and resources so that Britain might concentrate on what he held to be the vital spheres: Canada and the
Pitt's particular genius was to finance an army on the continent to drain French men and resources so that Britain might concentrate on what he held to be the vital spheres: Canada and the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
; whilst Clive successfully defeated Siraj ud-Daulah
Mirza Muhammad Siraj-ud-Daulah ( fa, ; 1733 – 2 July 1757), commonly known as Siraj-ud-Daulah or Siraj ud-Daula, was the last independent Nawab of Bengal. The end of his reign marked the start of the rule of the East India Company over Beng ...
, (the last independent Nawab of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, ...
) at Plassey
Palashi or Plassey ( bn, পলাশী, Palāśī, translit-std=ISO, , ) is a village on the east bank of Bhagirathi River, located approximately 50 kilometres north of the city of Krishnanagar in Kaliganj CD Block in the Nadia Distric ...
(1757), securing India. The Continental campaign was carried on by Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. From 19 ...
, defeated at Hastenbeck and forced to surrender at Convention of Klosterzeven
The Convention of Klosterzeven (or the Convention of Kloster-Zeven, german: Konvention von Kloster Zeven) was a convention signed on 10 September 1757 at Klosterzeven between France and the Electorate of Hanover during the Seven Years' War that ...
(1757) and thereafter by Ferdinand of Brunswick
Ferdinand is a Germanic name composed of the elements "protection", "peace" (PIE "to love, to make peace") or alternatively "journey, travel", Proto-Germanic , abstract noun from root "to fare, travel" (PIE , "to lead, pass over"), and "co ...
, later victor at Minden
Minden () is a middle-sized town in the very north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, the greatest town between Bielefeld and Hanover. It is the capital of the district (''Kreis'') of Minden-Lübbecke, which is part of the region of Detm ...
; Britain's Continental campaign had two major strands, firstly subsidising allies, particularly Frederick the Great, and second, financing an army to divert French resources from the colonial war and to also defend Hanover (which was the territory of the Kings of England at this time)
Pitt, was a leading Imperialist in English history. He was the directing mind in the expansion of his country, and with him the beginning of empire is rightly associated. The Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
might well, moreover, have been another Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
if Pitt had not furnished Frederick with an annual subsidy of £700,000, and in addition relieved him of the task of defending western Germany against France: this was the policy that allowed Pitt to boast of having "won Canada on the banks of the Rhine".
Contemporary opinion was, of course, incompetent to estimate the permanent results gained for the country by the brilliant foreign policy of Pitt. It has long been generally agreed that by several of his most costly expeditions nothing was really won but glory: the policy of diversionary attacks on places like Rochefort
Rochefort () may refer to:
Places France
* Rochefort, Charente-Maritime, in the Charente-Maritime department
** Arsenal de Rochefort, a former naval base and dockyard
* Rochefort, Savoie in the Savoie department
* Rochefort-du-Gard, in the Ga ...
was memorably described as 'breaking windows with gold guineas'. It has even been said that the only permanent acquisition that England owed directly to him was her Canadian dominion; and, strictly speaking, this is true, it being admitted that the campaign by which the Indian empire was virtually won was not planned by him, though brought to a successful issue during his ministry.
But material ''aggrandisement'', though the only tangible, was not the only real or lasting effect of a war policy. More could be gained by crushing a formidable rival than by conquering a province. The loss of her Canadian possessions was only one of a series of disasters suffered by France, which included the victories at sea of Boscawen at Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
and Hawke at Quiberon Bay
Quiberon Bay (french: Baie de Quiberon) is an area of sheltered water on the south coast of Brittany. The bay is in the Morbihan département.
Geography
The bay is roughly triangular in shape, open to the south with the Gulf of Morbihan to t ...
. Such defeats radically affected the future of Europe and the world. Deprived of her most valuable colonies both in the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
and in the West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
, and thoroughly defeated on the continent, France's humiliation was the beginning of a new epoch in history.
The victorious policy of Pitt destroyed the military prestige which repeated experience has shown to be in France as in no other country the very life of monarchy, and thus was not the least of the influences that slowly brought about the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
. It effectually deprived France of the lead in the councils of Europe which she had hitherto arrogated to herself, and so affected the whole course of continental politics. It is such far-reaching results as these, and not the mere acquisition of a single colony, however valuable, that constitute Pitt's claim to be considered as the most powerful minister that ever guided the foreign policy of England.
Resignation
 George II died on 25 October 1760, and was succeeded by his grandson,
George II died on 25 October 1760, and was succeeded by his grandson, George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
. The new king was inclined to view politics in personal terms and taught to believe that "Pitt had the blackest of hearts". The new king had counsellors of his own, led by Lord Bute
John Stuart, 3rd Earl of Bute, (; 25 May 1713 – 10 March 1792), styled Lord Mount Stuart between 1713 and 1723, was a British nobleman who served as the 7th Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1762 to 1763 under George III. He was arguabl ...
. Bute soon joined the cabinet as a Northern Secretary
The Secretary of State for the Northern Department was a position in the Cabinet of the government of Great Britain up to 1782, when the Northern Department became the Foreign Office.
History
Before the Act of Union, 1707, the Secretary of S ...
and Pitt and he were quickly in dispute over a number of issues.
In 1761 Pitt had received information from his agents about a secret Bourbon Family Compact
The ''Pacte de Famille'' (, ''Family Compact''; es, Pacto de Familia) is one of three separate, but similar alliances between the Bourbon kings of France and Spain. As part of the settlement of the War of the Spanish Succession that brought t ...
by which the Bourbons
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spanish ...
of France and Spain bound themselves in an offensive alliance against Britain. Spain was concerned that Britain's victories over France had left them too powerful, and were a threat in the long term to Spain's own empire. Equally they may have believed that the British had become overstretched by fighting a global war and decided to try to seize British possessions such as Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
. A secret convention pledged that if Britain and France were still at war by 1 May 1762, Spain would enter the war on the French side.
Pitt urged that such a clear threat should be met by a pre-emptive strike against Spain's navy and her colonies—with emphasis on speed to prevent Spain bringing the annual Manila galleon
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire) ...
safely to harbour. Bute and Newcastle refused to support such a move, as did the entire cabinet except Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
, believing it would make Britain look the aggressor against Spain potentially provoking other neutral nations to declare war on Britain. Pitt believed he had no choice but to leave a cabinet in which his advice on a vital question had been rejected and presented his resignation. Many of his cabinet colleagues secretly welcomed his departure as they believed his dominance and popularity were a threat to the Constitution. Pitt's brother-in-law George Grenville
George Grenville (14 October 1712 – 13 November 1770) was a British Whig statesman who rose to the position of Prime Minister of Great Britain. Grenville was born into an influential political family and first entered Parliament in 1741 as an ...
was given a major role in government, angering Pitt who felt Grenville should have resigned with him. Pitt regarded Grenville's action as a betrayal and there was hostility between them for several years.
After Pitt's resignation in October 1761, the King urged Pitt to accept a mark of royal favour. Accordingly, he obtained a pension of £3000 a year and his wife, Lady Hester Grenville was created Baroness Chatham in her own right—although Pitt refused to accept a title himself. Pitt assured the King that he would not go into direct opposition against the government. His conduct after his retirement was distinguished by a moderation and disinterestedness which, as Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS">New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS/nowiki>_1729_–_9_July_1797)_was_an_ NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style"> ...
remarked, "set a seal upon his character". The war with Spain, in which he had urged the cabinet to take the initiative, proved inevitable; but he scorned to use the occasion for "altercation and recrimination", and spoke in support of the government measures for carrying on the war.
Twenty years after he had received a similar windfall from the Marlborough legacy, Sir William Pynsent, Bt., a Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
baronet
A baronet ( or ; abbreviated Bart or Bt) or the female equivalent, a baronetess (, , or ; abbreviation Btss), is the holder of a baronetcy, a hereditary title awarded by the British Crown. The title of baronet is mentioned as early as the 14th ...
to whom he was personally quite unknown, left him his entire estate, worth about three thousand a year, in testimony of approval of his political career.
The Chatham Ministry
In July 1766 Rockingham was dismissed, and Pitt was entrusted by the King with the task of forming a government entirely of his own selection. His principle, "measures not men", appealed to the King whom he proposed to serve by "destroying all party distinctions". Pitt made appointments based not on connections but on merit, such asCharles Townshend
Charles Townshend (28 August 1725 – 4 September 1767) was a British politician who held various titles in the Parliament of Great Britain. His establishment of the controversial Townshend Acts is considered one of the key causes of the Ame ...
to the Exchequer
In the civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty’s Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's ''current account'' (i.e., money held from taxation and other government reven ...
and Shelburne as Secretary of State, to order American affairs. Pitt chose for himself the office of Lord Privy Seal
The Lord Privy Seal (or, more formally, the Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal) is the fifth of the Great Officers of State (United Kingdom), Great Officers of State in the United Kingdom, ranking beneath the Lord President of the Council and abov ...
, which required his elevation to the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
, and on 4 August he became Earl of Chatham
Chatham may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions Canada
* Chatham Islands (British Columbia)
* Chatham Sound, British Columbia
* Chatham, New Brunswick, a former town, now a neighbourhood of Miramichi
* Chatham (electoral district), New Brunswic ...
in the county of Kent and Viscount Pitt of Burton Pynsent
Curry Rivel is a village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated west of Somerton and east of Taunton in the South Somerset district. The parish has a population of 2,148. The parish includes the hamlet of Burton Pynsent.
History
The ...
in the county of Somerset.
Pitt's decision to accept a peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks.
Peerages include:
Australia
* Australian peers
Belgium
* Belgi ...
was likely influenced by his declining health and desire for a less demanding role, but the "great commoner" lost a great deal of public support. For example, in view of his probable accession to power, preparations were made in the City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London fr ...
for a banquet and a general illumination to celebrate the event, but the celebration was at once countermanded when it was known that he had become Earl of Chatham.
Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS">New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS/nowiki>_1729_–_9_July_1797)_was_an_ NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style"> ...
described the administration as "chequered and speckled", and spoke of it as "patriots and courtiers, King's friends and republicans; Whigs and Tories ... indeed a very curious show, but utterly unsafe to touch and unsure to stand on".
The problems facing the government included the observance of the Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
by France and Spain, tension between American colonists and the mother country, and the status of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
. One of the new ministry's earliest acts was to lay an embargo
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstances—they m ...
upon corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, which was thought necessary in order to prevent a dearth resulting from the unprecedented bad harvest of 1766. The measure was strongly opposed, and Lord Chatham delivered his first speech in the House of Lords in support of it. It proved to be almost the only measure introduced by his government in which he personally interested himself.
In 1767, Charles Townshend, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, enacted duties
A duty (from "due" meaning "that which is owing"; fro, deu, did, past participle of ''devoir''; la, debere, debitum, whence "debt") is a commitment or expectation to perform some action in general or if certain circumstances arise. A duty may ...
in the American colonies on tea, paper, and other goods. The taxes were created without the consultation of Chatham and possibly against his wishes. They proved offensive to the American colonists. Chatham's attention had been directed to the growing importance of the affairs of India, and there is evidence in his correspondence that he was meditating a comprehensive scheme for transferring much of the power of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
to the crown. Yet he was incapacitated physically and mentally during nearly his entire tenure of office. Chatham rarely saw any of his colleagues though they repeatedly and urgently pressed for interviews with him, and even an offer from the King to visit him in person was respectfully declined. While his gout seemed to improve, he was newly afflicted with mental alienation bordering on insanity
Insanity, madness, lunacy, and craziness are behaviors performed by certain abnormal mental or behavioral patterns. Insanity can be manifest as violations of societal norms, including a person or persons becoming a danger to themselves or to ...
. Chatham's lack of leadership resulted in an incohesive set of policies.
Chatham dismissed his allies Amherst Amherst may refer to:
People
* Amherst (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Earl Amherst of Arracan in the East Indies, a title in the British Peerage; formerly ''Baron Amherst''
* Baron Amherst of Hackney of the City of London, ...
and Shelburne from their posts, and then in October 1768 he tendered his own resignation on the grounds of poor health, leaving the leadership to Grafton, his First Lord of the Treasury
The first lord of the Treasury is the head of the Lords Commissioners of the Treasury exercising the ancient office of Lord High Treasurer in the United Kingdom, and is by convention also the prime minister. This office is not equivalent to the ...
.
Later life

Falklands Crisis
The same year when Britain and Spain became involved in the Falklands Crisis and came close to war, Pitt was a staunch advocate of taking a tough stance with Madrid and Paris (as he had been during the earlierCorsican Crisis
The Corsican Crisis was an event in British politics during 1768–69. It was precipitated by the invasion of the island of Corsica by France. The British government under the Duke of Grafton failed to intervene, for which it was widely criticised ...
when France had invaded Corsica) and made a number of speeches on the subject rousing public opinion. The government of Lord North
Frederick North, 2nd Earl of Guilford (13 April 17325 August 1792), better known by his courtesy title Lord North, which he used from 1752 to 1790, was 12th Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1770 to 1782. He led Great Britain through most o ...
was pushed into taking a firmer line because of this, mobilising the navy, and forcing Spain to back down. Some had even believed that the issue was enough to cast North from office and restore Pitt as Prime Minister—although the ultimate result was to strengthen the position of North who took credit for his firm handling of the crisis and was able to fill the cabinet with his own supporters. North would go on to dominate politics for the next decade, leading the country until 1782.
War of American Independence
Chatham sought to find a compromise on the escalating conflict with the American colonies. As he realised the gravity of the American situation, Chatham re-entered the fray, declaring that he would "be in earnest for the public" and "a scarecrow of violence to the gentler warblers of the grove". His position changed from an obsession in 1774 with the question of the authority of Parliament to a search for a formula for conciliation in 1775. He proposed the "Provisional Act" that would both maintain the ultimate authority of Parliamentary sovereignty, while meeting the colonial demands. The Lords defeated his proposal on 1 February 1775. Chatham's warnings regarding America were ignored. His brave efforts to present his case, passionate, deeply pondered, for the concession of fundamental liberties—no taxation without consent, independent judges, trial by jury, along with the recognition of the AmericanContinental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
—foundered on the arrogance and complacency of his peers.
After war had broken out, he warned that America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
could not be conquered. Due to his stance, Pitt was very popular amongst the American colonists. This high esteem approached to idolatry according to historian Clinton Rossiter
Clinton Lawrence Rossiter III (September 18, 1917 – July 11, 1970) was an American historian and political scientist at Cornell University (1947-1970) who wrote ''The American Presidency'', among 20 other books, and won both the Bancroft Prize a ...
:
In the last decade of the colonial period the ideal of the man of public virtue was made real in the person of William Pitt. The cult of this noblest of Whigs, "the Genius of England and the Comet of his Age" was well advanced toward idolatry at least five years before the Stamp Act. The greatest of "the great men of England", the last and noblest of the Romans, was considered the embodiment of virtue, wisdom, patriotism, liberty, and temperance ... Pitt, "glorious and immortal", the "guardian of America", was the idol of the colonies ... A Son of Liberty in Bristol County, Massachusetts, paid him the ultimate tribute of identification with English liberty: "Our toast in general is,—''Magna Charta'', the ''British Constitution'',—PITT and Liberty forever!"
Death
 Pitt had now almost no personal following, mainly owing to the grave mistake he had made in not forming an alliance with the Rockingham party, but his eloquence was as powerful as ever, and all its power was directed against the government policy in the contest with America, which had become the question of all-absorbing interest. His last appearance in the House of Lords was on 7 April 1778, on the occasion of the
Pitt had now almost no personal following, mainly owing to the grave mistake he had made in not forming an alliance with the Rockingham party, but his eloquence was as powerful as ever, and all its power was directed against the government policy in the contest with America, which had become the question of all-absorbing interest. His last appearance in the House of Lords was on 7 April 1778, on the occasion of the Duke of Richmond
Duke of Richmond is a title in the Peerage of England that has been created four times in British history. It has been held by members of the royal Tudor dynasty, Tudor and House of Stuart, Stuart families.
The current dukedom of Richmond was ...
's motion for an address praying the king to conclude peace with America on any terms.
In view of the hostile demonstrations of France the various parties had come generally to see the necessity of such a measure but Chatham could not brook the thought of a step which implied submission to the "natural enemy" whom it had been the main object of his life to humble, and he declaimed for a considerable time, though with diminished vigour, against the motion. After the Duke of Richmond had replied, he rose again excitedly as if to speak, pressed his hand upon his breast, and fell down in a fit. His last words before he collapsed were: "My Lords, any state is better than despair; if we must fall, let us fall like men." James Harris MP, however, recorded that Lord Nugent had told him that Chatham's last words in the Lords were: "If the Americans defend independence, they shall find me in their way" and that his very last words (spoken to his soldier son John) were: "Leave your dying father, and go to the defence of your country".
He was moved to his home at Hayes, where his middle son William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
read to him Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's passage about the death of Hector
In Greek mythology, Hector (; grc, Ἕκτωρ, Hektōr, label=none, ) is a character in Homer's Iliad. He was a Trojan prince and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. Hector led the Trojans and their allies in the defense o ...
. Chatham died on 11 May 1778, aged 69. Although he was initially buried at Hayes, with graceful unanimity all parties combined to show their sense of the national loss and the Commons presented an address to the king praying that the deceased statesman might be buried with the honours of a public funeral. A sum was voted for a public monument which was erected over a new grave in Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
. The monument, by the sculptor John Bacon, has a figure of Pitt above statues of Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
with figures representing Prudence, Fortitude, the Earth and also a sea creature.
In the Guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a "guild hall" or "guild house", is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commonly become town halls and in som ...
Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS">New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS/nowiki>_1729_–_9_July_1797)_was_an_ NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style"> ...
's inscription summed up what he had meant to the city: he was "the minister by whom commerce was united with and made to flourish by war". Soon after the funeral a bill was passed bestowing a pension of £4,000 a year on his successors in the earldom
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant "chieftain", particular ...
. He had a family of three sons and two daughters, of whom the second son, William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, was destined to add fresh lustre to a name that many regarded as one of the greatest in the history of England.
Legacy

Horace Walpole
Horatio Walpole (), 4th Earl of Orford (24 September 1717 – 2 March 1797), better known as Horace Walpole, was an English writer, art historian, man of letters, antiquarian, and Whigs (British political party), Whig politician.
He had Strawb ...
, not an uncritical admirer, wrote of Pitt:
It were ingratitude to him to say that he did not give such a reverberation to our stagnating councils, as exceedingly altered the appearance of our fortune. He warded off the evil hour that seemed approaching, he infused vigour into our arms, he taught the nation to speak again as England used to speak to foreign powers ... Pitt, on entering upon administration, had found the nation at the lowest ebb in point of power and reputation ... France, who meant to be feared, was feared heartily ... They were willing to trust that France would be so good as to ruin us by inches. Pitt had roused us from this ignoble lethargy ... The admirers of Mr Pitt extol the reverberation he gave to our councils, the despondence he banished, the spirit he infused, the conquests he made, the security he affixed to our trade and plantations, the humiliation of France, the glory of Britain carried under his administration to a pitch at which it never had arrived—and all this is exactly true.
Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. The ''Oxford ...
is reported to have said that "Walpole was a minister given by the king to the people, but Pitt was a minister given by the people to the king", and the remark correctly indicated Chatham's distinctive place among English statesmen. He was the first minister whose main strength lay in the support of the nation at large as distinct from its representatives in the Commons, where his personal following was always small. He was the first to discern that public opinion, though generally slow to form and slow to act, is in the end the paramount power in the state; and he was the first to use it not in an emergency merely, but throughout a whole political career.
Chatham marked the commencement of that vast change in the movement of English politics
Politics of England forms the major part of the wider politics of the United Kingdom, with England being more populous than all the other countries of the United Kingdom put together. As England is also by far the largest in terms of area and ...
by which it came about that the sentiment of the great mass of the people then told effectively on the action of the government from day to day—almost from hour to hour. He was well fitted to secure the sympathy and admiration of his countrymen, for his virtues and his failings were alike English. He was often inconsistent, he was generally intractable and overbearing, and he was always pompous and affected to a degree which, as Macaulay remarked, seemed scarcely compatible with true greatness.
Of the last quality evidence was furnished in the stilted style of his letters, and in the fact recorded by Thomas Seward
Thomas Seward (1708 – 4 March 1790) was an English Anglican clergyman, author and editor who was part of the Lichfield intellectual circle that included Samuel Johnson, Erasmus Darwin and his own daughter Anna Seward, amongst others.
Life
Tho ...
that he never permitted his under-secretaries to sit in his presence. Burke spoke of "some significant, pompous, creeping, explanatory, ambiguous matter, in the true Chathamic style". But these defects were known only to the inner circle of his associates.
To the outside public he was endeared as a statesman who could do or suffer "nothing base", and who had the rare power of transfusing his own indomitable energy and courage into all who served under him. "A spirited foreign policy" has always been popular in England, and Pitt was the most popular of English ministers, because he was the most successful exponent of such a policy. In domestic affairs his influence was small and almost entirely indirect. He himself confessed his unfitness for dealing with questions of finance. The commercial prosperity that was produced by his war policy was in a great part delusive, as prosperity so produced must always be, though it had permanent effects of the highest moment in the rise of such centres of industry as Glasgow. This, however, was a remote result which he could have neither intended nor foreseen.
It has been suggested that Pitt was in fact a far more orthodox Whig than has been historically portrayed demonstrated by his sitting for rotten borough seats controlled by aristocratic magnates, and his lifelong concern for protecting the balance of power on the European continent, which marked him out from many other Patriots.
Historians have described Pitt as "the greatest British statesman of the eighteenth century". He is immortalised in St Stephen's Hall
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank ...
, where he and other notable Parliamentarians look on at visitors to Parliament.parliament.uk: "Architecture of the Palace – St Stephen's Hall"/ref> The American city of
Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, originally Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
, was renamed for Pitt after it was captured from the French during the Seven Years' War.
Family and personal life
Pitt married Lady Hester Grenville (1720–1803), daughter of the 1st Countess Temple, on 16 November 1754 byFrancis Ayscough
Francis Ayscough (1701–1763) was a tutor to George III and Clerk of the Closet to his father Frederick, Prince of Wales
under special licence at her home in Argyle Street, London
Argyll Street is a road located in the Soho district of Central London. It links Great Marlborough Street to the south to Oxford Street in the north and is connected to Regent Street to the west by Little Argyll Street. Historically it was someti ...
.
They had five children, born at Hayes:
* Lady Hester Pitt (19 October 175520 July 1780), who married Viscount Mahon, later the 3rd Earl Stanhope
Earl Stanhope ()Debrett's Correct Form, Debrett's Peerage Ltd, 1976, pg 408 was a title in the Peerage of Great Britain. The earldom was created in 1718 for Major General James Stanhope,Edward Hasted, 'Parishes: Chevening', in The History and To ...
, on 19 December 1774; three children, including the traveler and Arabist Lady Hester Stanhope
Lady Hester Lucy Stanhope (12 March 1776 – 23 June 1839) was a British aristocrat, adventurer, antiquarian, and one of the most famous travellers of her age. Her archaeological excavation of Ashkelon in 1815 is considered the first to ...
* John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham
General John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham, also 2nd Viscount Pitt and 2nd Baron Chatham, (9 October 1756 – 24 September 1835) was a British soldier and politician. He spent a lengthy period in the cabinet but is best known for commanding the dis ...
(1756–1835), who married The Hon. Mary Townshend; no issue
* Lady Harriet Pitt (18 April 1758 – 1786), who married The Hon. Edward James Eliot, oldest son of the 1st Baron Eliot, in 1785; one child
* Hon. William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ire ...
(28 May 1759 – 23 January 1806), who also served as Prime Minister; never married
* Hon. James Charles Pitt (24 April 176113 November 1780), Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
officer who died in Antigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
; never married
Cultural references
There have been at least twoRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
ships that bore the name HMS Pitt.
Places named after William Pitt
United States *Chatham Strait
Chatham Strait, or Shee ya xhaak in the Tlingit language, is a narrow passage of the Alexander Archipelago in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Alaska. It separates Chichagof Island and Baranof Island to its west from Admiralty Island ...
, Alaska
* Chatham, Virginia
Chatham is a town in Pittsylvania County, Virginia, Pittsylvania County, Virginia, United States. It is the county seat of Pittsylvania County, Virginia, Pittsylvania County. Chatham's population was 1,269 at the 2010 census. It is included in the ...
* Chatham, New Hampshire
Chatham is a town in Carroll County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 341 at the 2020 census. It is located in the White Mountains, and except for the southeast corner, all of Chatham is in the White Mountain National Forest. The ...
* Chatham, New Jersey
"The Chathams" is a term used in reference to shared services for two neighboring municipalities in Morris County, New Jersey, Morris County, New Jersey, United States – Chatham Borough, New Jersey, Chatham Borough and Chatham Township, New Jers ...
* Chatham County, Georgia
Chatham County ( ) is located in the U.S. state of Georgia, on the state's Atlantic coast. The county seat and largest city is Savannah. One of the original counties of Georgia, Chatham County was created February 5, 1777, and is named after Will ...
* Chatham Square
Chatham Square is a major intersection in Chinatown, Manhattan, New York City. The square lies at the confluence of eight streets: the Bowery, Doyers Street, East Broadway, St. James Place, Mott Street, Oliver Street, Worth Street and Park R ...
, Savannah, Georgia
* Pitt County, North Carolina
Pitt County is a county located in the inner banks (northeastern part) of the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 170,243, making it the fourteenth-most populous county in North Carolina. Its county seat is ...
* Chatham County, North Carolina
Chatham County ( )
, from the North Carolina Collection's website at the
"Lines To A Gentleman"
which Burns composed in response to being sent a newspaper, which the gentlemen sender offered to continue providing free of charge. The poet's satirical summary of events makes clear that he has no interest in the reports contained in the newspaper. The poem's section on events in Parliament, which refers to Pitt as 'Chatham Will', is as follows:
online
older classic recommended by Jeremy Black (1992) * Sherrard, O. A. ''Lord Chatham: A War Minister in the Making; Pitt and the Seven Years War; and America'' (3 vols, The Bodley Head, 1952–58) * * Williams, Basil. ''
vol 1 onlinevol 2 online free
online
587pp; useful old classic, strong on politics 1714–1815. * Robertson, Charles. Grant ''Chatham and the British empire'' (1948
online
* Rodger N. A. M. ''Command of the Ocean: A Naval History of Britain, 1649–1815''. Penguin Books, 2006. * * Trench, Chenevix Charles. ''George II''. Allen Lane, 1973 * Turner, Michael J. ''Pitt the Younger: A Life''. Hambledon & London, 2003. * Williams, Basil. '' "The Whig Supremacy, 1714–1760'' (2nd ed. 1962) pp 354–77, on his roles 1756–63. * Wolfe, Eugene L. ''Dangerous Seats: Parliamentary Violence in the United Kingdom'' Amberley, 2019. * Woodfine, Philip. ''Britannia's Glories: The Walpole Ministry and the 1739 War with Spain''. Boydell Press, 1998.
More about The Earl of Chatham, William Pitt 'The Elder'
on the Downing Street website.
William Pitt's Defense of the American Colonies
Bronze Bust of William Pitt
by
, from the North Carolina Collection's website at the
Pittsburg, New Hampshire
Pittsburg is a town in Coös County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 800 at the 2020 census. It is the northernmost town in New Hampshire and the largest town by area in New England. U.S. Route 3 is the only major highway in th ...
* Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, Pennsylvania (renamed, previously called Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
). After British General John Forbes occupied Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed a ...
during the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
, he ordered the site's reconstruction and named it after then-Secretary of State Pitt. He also named the settlement between the rivers "Pittsborough", which would eventually become known as Pittsburgh.
* Chatham University
Chatham University is a private university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Originally founded as a women's college, it began enrolling men in undergraduate programs in 2015. It enrolls about 2,110 students, including 1,002 undergraduate students an ...
, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
* Chatham, Massachusetts
Chatham () is a town in Barnstable County, Massachusetts, United States. Chatham is located at the southeast tip of Cape Cod and has historically been a fishing community. First settled by the English in 1664, the township was originally called Mo ...
* Pittsfield, Massachusetts
Pittsfield is the largest city and the county seat of Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the principal city of the Pittsfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses all of Berkshire County. Pittsfield� ...
* Pittsfield, New Hampshire
Pittsfield is a town in Merrimack County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 4,075 at the 2020 census.
The main village in town, where 1,570 people resided at the 2020 census, is defined as the Pittsfield census-designated place (C ...
* Pittsfield Charter Township, Michigan
Pittsfield Charter Township is a charter township of Washtenaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 34,663 at the 2010 census.
Communities
* Lucerne is a former settlement within the township that had its own post office from ...
* Pittsgrove Township, New Jersey
Pittsgrove Township is a township in Salem County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2010 United States Census, the township's population was 9,393, reflecting an increase of 500 (+5.6%) from the 8,893 counted in the 2000 Census, whic ...
* Pittstown, New Jersey
* Pittston, Pennsylvania
Pittston is a city in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is situated between Scranton, Pennsylvania, Scranton and Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Wilkes-Barre in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The city gained prominence in the late 19th an ...
* Pittston Township, Pennsylvania
Pittston Township is a township in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania. The population was 3,179 as of the 2020 census. The township is located within the Greater Pittston region. As of 2010, the total population of Greater Pittston was 48,020. The Wilkes ...
* Pittsylvania County, Virginia
Pittsylvania County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 60,501. Chatham is the county seat.
Pittsylvania County is included in the Danville, VA Micropolitan Statistical Ar ...
, and its county seat, Chatham
Chatham may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions Canada
* Chatham Islands (British Columbia)
* Chatham Sound, British Columbia
* Chatham, New Brunswick, a former town, now a neighbourhood of Miramichi
* Chatham (electoral district), New Brunswic ...
* Pittsboro, North Carolina
Pittsboro is a town in Chatham County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 3,743 at the 2010 census and 4,537 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Chatham County.
The town was established in the late 18th century, shortly a ...
* Chatham Square
Chatham Square is a major intersection in Chinatown, Manhattan, New York City. The square lies at the confluence of eight streets: the Bowery, Doyers Street, East Broadway, St. James Place, Mott Street, Oliver Street, Worth Street and Park R ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
*The short-lived, sparsely-colonised, extralegal colony of Vandalia (located in modern West Virginia and named after Queen Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz) was originally named Pittsylvania after Pitt.
Canada
* Chatham Township, Quebec.
* Chatham, Ontario
* CFB Chatham
Canadian Forces Base Chatham or CFB Chatham was a Canadian Forces Base located immediately south of the town of Chatham, New Brunswick, Canada. Parts are now operating as Miramichi Municipal Airport since 1974 with a partial runway available ( ...
, near Chatham, New Brunswick
Chatham is an urban neighbourhood in the city of Miramichi, New Brunswick, Canada.
Prior to municipal amalgamation in 1995, Chatham was an incorporated town in Northumberland County along the south bank of the Miramichi River opposite Douglasto ...
Australia
* Pitt Town, New South Wales
Pitt Town is a historic town and suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Pitt Town is 59 kilometres north-west of the Sydney central business district in the local government area of the City of Hawkesbury. It is bound ...
, named after Pitt by Governor Macquarie
Major General Lachlan Macquarie, CB (; gd, Lachann MacGuaire; 31 January 1762 – 1 July 1824) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator from Scotland. Macquarie served as the fifth Governor of New South Wales from 1810 to 1821, an ...
in 1810
* Chatham, New South Wales
Ecuador
* Chatham Island
Chatham Island ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) is by far the largest island of the Chatham Islands group, in the south Pacific Ocean off the eastern coast of New Zealand's South Island. It is said to be "halfway bet ...
, Galápagos
New Zealand
* Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about te ...
an archipelago including Pitt Island
Pitt Island is the second largest island in the Chatham Islands, Chatham Archipelago, New Zealand. It is called ''Rangiauria'' in Māori language, Māori and ''Rangiaotea'' in ''Moriori language, Moriori.Government of New Zealand, Dept. of Cons ...
and Chatham Island
Chatham Island ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) is by far the largest island of the Chatham Islands group, in the south Pacific Ocean off the eastern coast of New Zealand's South Island. It is said to be "halfway bet ...
References in popular culture
* Pitt is referred to in the ''Simpsons
''The Simpsons'' is an American animated sitcom created by Matt Groening for the Fox Broadcasting Company. The series is a satirical depiction of American life, epitomized by the Simpson family, which consists of Homer, Marge, Bart, Lisa, a ...
'' episode "Homer at the Bat
"Homer at the Bat" is the seventeenth episode of the The Simpsons (season 3), third season of the American animated television series ''The Simpsons''. It originally aired on the Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox network in the United States on Februar ...
", where Barney
Barney may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Barney (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Barney (surname), a list of people
Film and television
* the title character of ''Barney & Friends'', an American live actio ...
and guest star Wade Boggs
Wade Anthony Boggs (born June 15, 1958) is an American former professional baseball third baseman. He spent 18 seasons in Major League Baseball, primarily with the Boston Red Sox. He also played for the New York Yankees (1993-1997), and the Tampa ...
get into a bar fight after a heated debate over the subject of who was England's greatest Prime Minister. Boggs claims Pitt the Elder was the greatest Prime Minister to Barney's Lord Palmerston
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, (20 October 1784 – 18 October 1865) was a British statesman who was twice Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in the mid-19th century. Palmerston dominated British foreign policy during the period ...
, causing Barney to punch Boggs in the face, knocking him unconscious.
* Pitt is briefly derided (but does not appear) in the ''Blackadder The Third'' episode "Dish and Dishonesty
''Blackadder the Third'' is the third series of the BBC sitcom '' Blackadder'', written by Richard Curtis and Ben Elton, which aired from 17 September to 22 October 1987. The series is set during the Georgian Era, and sees the principal chara ...
". Blackadder states that he is "about as effective as a catflap in an elephant house".
* In ''The Two Georges
''The Two Georges'' is an alternate history and detective thriller novel co-written by science fiction author Harry Turtledove and Oscar-winning actor Richard Dreyfuss. It was originally published in 1995 by Hodder & Stoughton in the United King ...
'', an alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, altern ...
by Harry Turtledove
Harry Norman Turtledove (born June 14, 1949) is an American author who is best known for his work in the genres of alternate history, historical fiction, fantasy, science fiction, and mystery fiction. He is a student of history and completed ...
, William Pitt was the Prime Minister during a period of political tension between Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and its North American colonies. He played a significant role in easing those tensions and ensuring the colonists remained content British subjects. He was also one of the historical figures in Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of ...
's fictional painting ''The Two Georges'', depicting George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
being presented to King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
.
* In 1770, Laurence Sterne
Laurence Sterne (24 November 1713 – 18 March 1768), was an Anglo-Irish novelist and Anglican cleric who wrote the novels ''The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman'' and ''A Sentimental Journey Through France and Italy'', published ...
dedicated his masterpiece, ''The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman
''The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman'', also known as ''Tristram Shandy'', is a novel by Laurence Sterne, inspired by ''Don Quixote''. It was published in nine volumes, the first two appearing in 1759, and seven others followin ...
'' to the rt. hon. Mr Pitt.Sterne, Laurence: The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts (1951). Page 28.
* In 1790, Scotland's Bard, the poet Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 175921 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the best known of the poets who hav ...
, referred to Pitt in his Scots language
Scots ( endonym: ''Scots''; gd, Albais, ) is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland (where the local dialect is known as Ulster Scots). Most commonly ...
poem"Lines To A Gentleman"
which Burns composed in response to being sent a newspaper, which the gentlemen sender offered to continue providing free of charge. The poet's satirical summary of events makes clear that he has no interest in the reports contained in the newspaper. The poem's section on events in Parliament, which refers to Pitt as 'Chatham Will', is as follows:
See also
*Grenvillite
The Grenville Whigs (or Grenvillites) were a name given to several British political factions of the 18th and the early 19th centuries, all of which were associated with the important Grenville family of Buckinghamshire.
Background
The Grenvi ...
Notes
Sources
*Further reading
Biographical
* * * Black, Jeremy. ''Pitt the Elder''. Cambridge University Press, 1992. * Brown, Peter Douglas. ''William Pitt, Earl of Chatham: The Great Commoner''. George Allen & Unwin, 1978. * * * Pearce, Edward. ''Pitt the Elder: Man of War'' (Random House, 2010). * * * Plumb, J. H. "The Earl of Chatham." ''History Today'' (1952) 2#3 pp 175–180 online * Ruville, Albert von. ''William Pitt, earl of Chatham'' (3 vols. 1907online
older classic recommended by Jeremy Black (1992) * Sherrard, O. A. ''Lord Chatham: A War Minister in the Making; Pitt and the Seven Years War; and America'' (3 vols, The Bodley Head, 1952–58) * * Williams, Basil. ''
The Life of William Pitt, Earl of Chatham
''The Life of William Pitt, Earl of Chatham'' is a two-volume biography of the British eighteenth-century statesman William Pitt, Earl of Chatham. Written by the historian Basil Williams it was originally published in 1913. It has remained a st ...
'' (2 vols, 1915vol 1 online
Specialised studies
* Anderson, Fred. ''Crucible of War: The Seven Years' War and the Fate of Empire in British North America, 1754–1766''. Faber and Faber, 2000. * Black, Jeremy, ed., ''Britain in the age of Walpole'' (1984) * Black, Jeremy. ''British Foreign Policy in the Age of Walpole'' (1985) * * Corbett, Julian Stafford ''England in the Seven Years' War'' (2 vol. 1907), military history * De-La-Noy, Michael. ''The King Who Never Was: The Story of Frederick, Prince of Wales''. Peter Owen, 1996. * Dull, Jonathan R. ''The French Navy and the Seven Years' War''. (University of Nebraska Press, 2005). * * Leonard, Dick. "William Pitt, the Elder, First Earl of Chatham—'I am Sure That I Can Save This Country, and That Nobody Else Can'." in Leonard, ''Eighteenth-Century British Premiers'' (Palgrave Macmillan UK, 2011), 129–153. * McLynn, Frank. ''1759: The Year Britain Became Master of the World''. Pimlico, 2000. * Middleton, Richard. ''The Bells of Victory: The Pitt-Newcastle Ministry and Conduct of the Seven Years' War 1757–1762'' (Cambridge UP, 2002). * * Peters, Marie. ''Pitt and Popularity: The Patriot Minister and London Opinion During the Seven Years' War'' (1981) 309pp * Robertson, Charles Grant. ''England under the Hanoverians'' (1911)online
587pp; useful old classic, strong on politics 1714–1815. * Robertson, Charles. Grant ''Chatham and the British empire'' (1948
online
* Rodger N. A. M. ''Command of the Ocean: A Naval History of Britain, 1649–1815''. Penguin Books, 2006. * * Trench, Chenevix Charles. ''George II''. Allen Lane, 1973 * Turner, Michael J. ''Pitt the Younger: A Life''. Hambledon & London, 2003. * Williams, Basil. '' "The Whig Supremacy, 1714–1760'' (2nd ed. 1962) pp 354–77, on his roles 1756–63. * Wolfe, Eugene L. ''Dangerous Seats: Parliamentary Violence in the United Kingdom'' Amberley, 2019. * Woodfine, Philip. ''Britannia's Glories: The Walpole Ministry and the 1739 War with Spain''. Boydell Press, 1998.
Historiography
* Moncure, James A. (ed.) ''Research Guide to European Historical Biography: 1450–Present'' (4 vol 1992); 4:1629–39 * *Primary sources
* *External links
* *More about The Earl of Chatham, William Pitt 'The Elder'
on the Downing Street website.
William Pitt's Defense of the American Colonies
Bronze Bust of William Pitt
by
William Reid Dick
Sir William Reid Dick, (13 January 1878 – 1 October 1961) was a Scottish sculptor known for his innovative stylisation of form in his monument sculptures and simplicity in his portraits. He became an Associate of the Royal Academy in 1921, a ...
(1922) to Pittsburgh Mayor William A. Magee
William Addison Magee (May 4, 1873 – March 25, 1938) was born in Pittsburgh's Hill District neighborhood near the site of the former Mellon Arena. Before becoming mayor he gained his reputation by serving as Assistant District Attorney for ...
, by Charles Wakefield, 1st Viscount Wakefield
Charles Cheers Wakefield, 1st Viscount Wakefield, GCVO, CBE (12 December 1859 – 15 January 1941), was an English businessman who founded the Castrol lubricants company, was lord mayor of London and was a significant philanthropist.
Early lif ...
* William Pitt Collection. General Collection, Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, Yale University.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chatham, William Pitt, 1st Earl Of
1708 births
1778 deaths
People from Westminster
Pitt, William
Alumni of Trinity College, Oxford
Pitt, William
British MPs 1734–1741
British MPs 1741–1747
British MPs 1747–1754
British MPs 1754–1761
British MPs 1761–1768
Prime Ministers of Great Britain
Secretaries of State for the Southern Department
Paymasters of the Forces
Lords Privy Seal
Whig (British political party) MPs for English constituencies
Members of the Privy Council of Great Britain
British people of the French and Indian War
Earls in the Peerage of Great Britain
Peers of Great Britain created by George III
Burials at Westminster Abbey
18th-century heads of government
Leaders of the House of Commons of Great Britain
Fellows of the Royal Society
William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
Parents of prime ministers of the United Kingdom
1st King's Dragoon Guards officers
British people of the Seven Years' War
MPs for rotten boroughs
Members of the Parliament of Great Britain for Okehampton